By reviewing this flashcard review list, you will gain a better understanding of the root words and combining forms associated with the skeletal system.
Check out the quiz version of this flashcard if you want to see how much you remember.
#1 ankyl/o
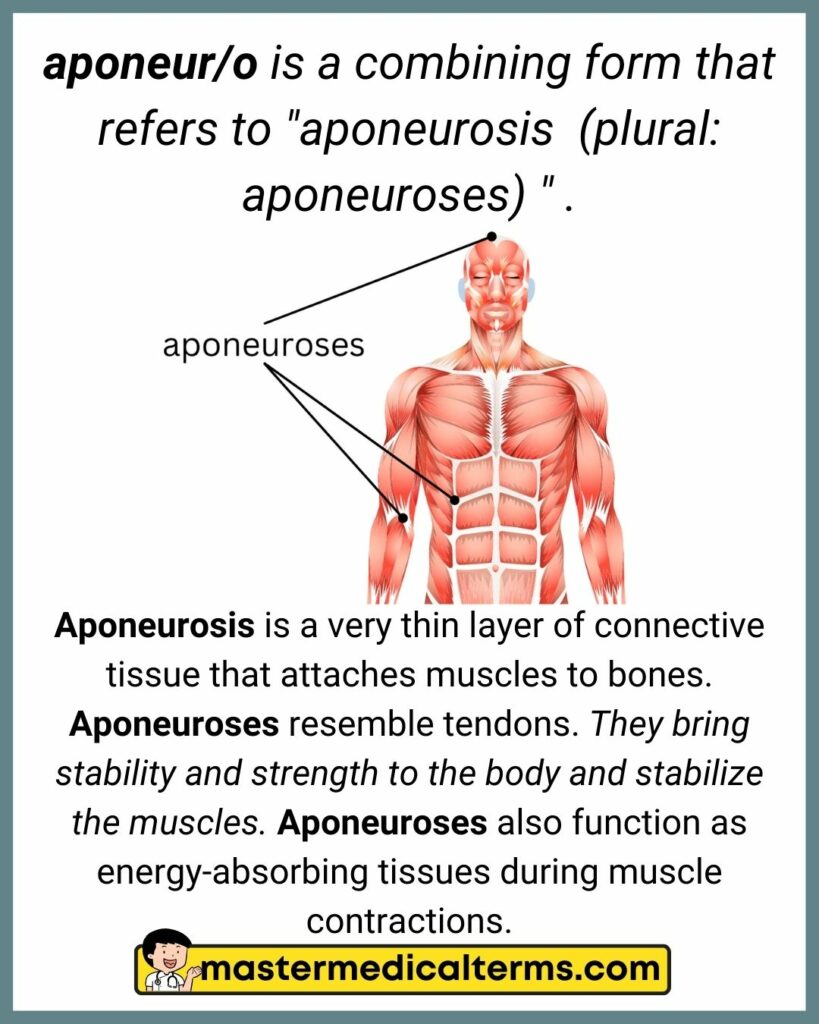
#2 aponeur/o
aponeur/o is a combining form that refers to "aponeurosis (plural: aponeuroses) " .
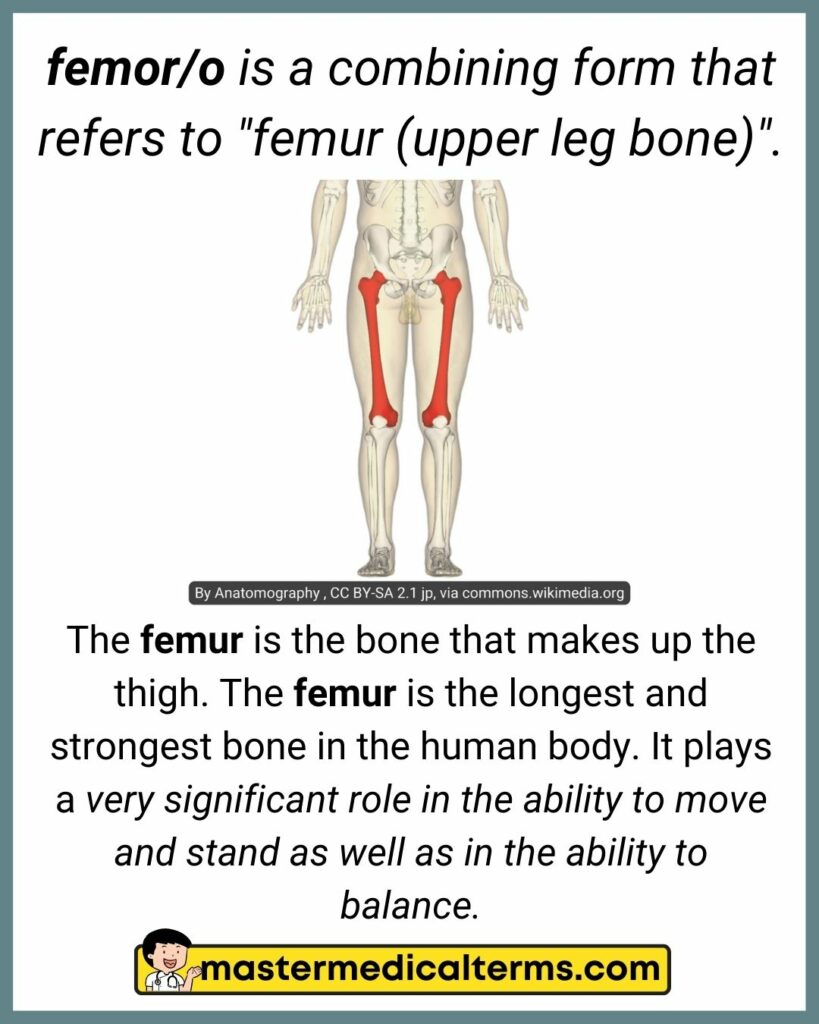
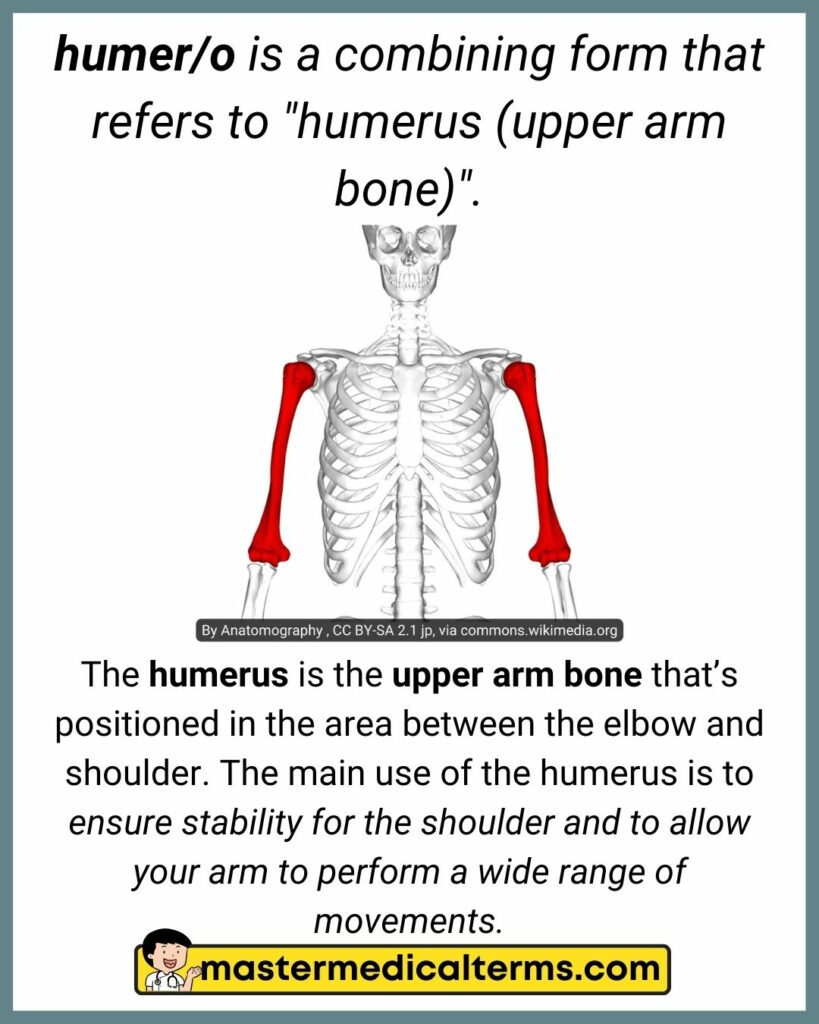
Aponeurosis is a very thin layer of connective tissue that attaches muscles to bones. Aponeuroses resemble tendons. They bring stability and strength to the body and stabilize the muscles. Aponeuroses also function as energy-absorbing tissues during muscle contractions.
#3 arthr/o
arthr/o is a combining form that refers to "joint".
A joint is a place where two or more bones meet at a point on their surface. The majority of joints are mobile, so the bones are able to move as a result. There are several components that make up a joint: cartilage, synovial membrane, ligaments, tendons, bursas, synovial fluid, and meniscus.
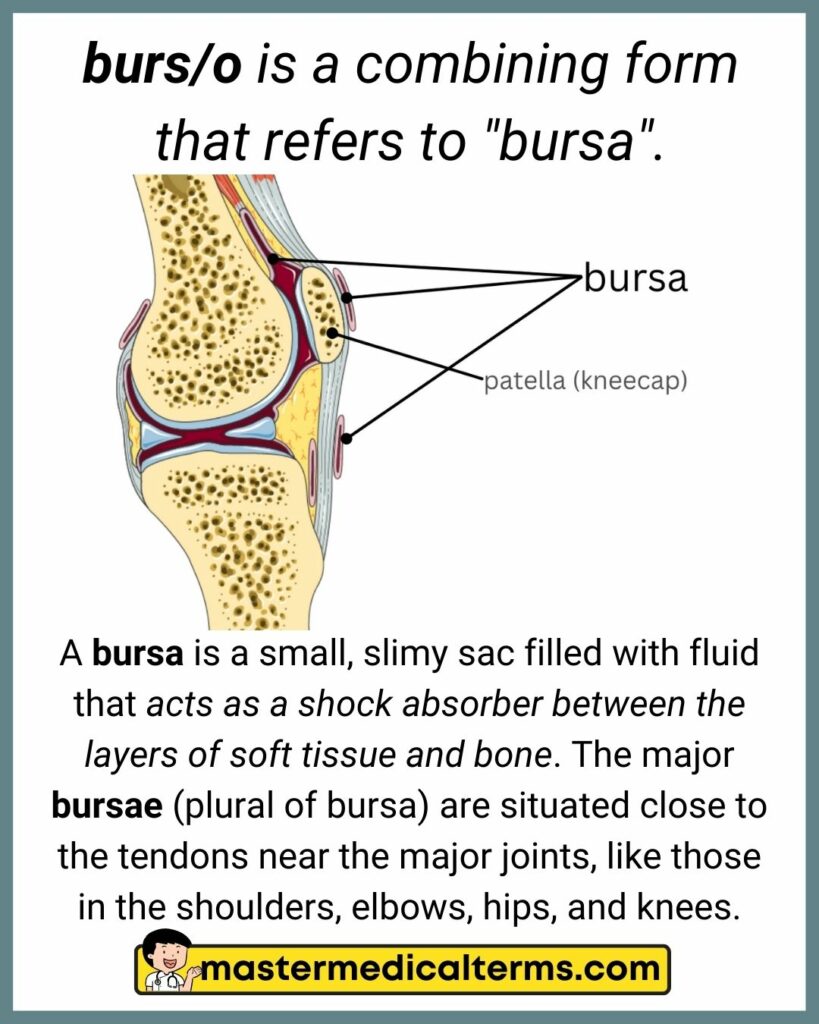
#4 burs/o
burs/o is a combining form that refers to "bursa".
A bursa is a small, slimy sac filled with fluid that acts as a shock absorber between the layers of soft tissue and bone. The major bursae (plural of bursa) are situated close to the tendons near the major joints, like those in the shoulders, elbows, hips, and knees.
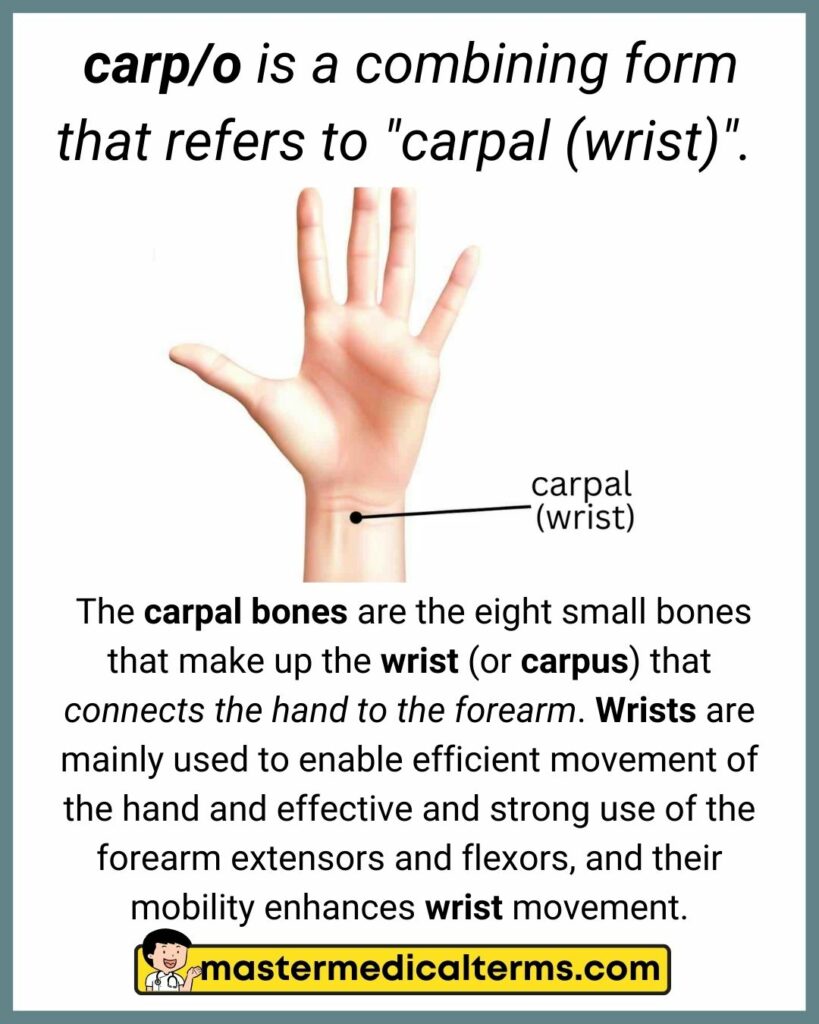
#5 carp/o
carp/o is a combining form that refers to "carpal (wrist)".
The carpal bones are the eight small bones that make up the wrist (or carpus) that connects the hand to the forearm. Wrists are mainly used to enable efficient movement of the hand and effective and strong use of the forearm extensors and flexors, and their mobility enhances wrist movement.
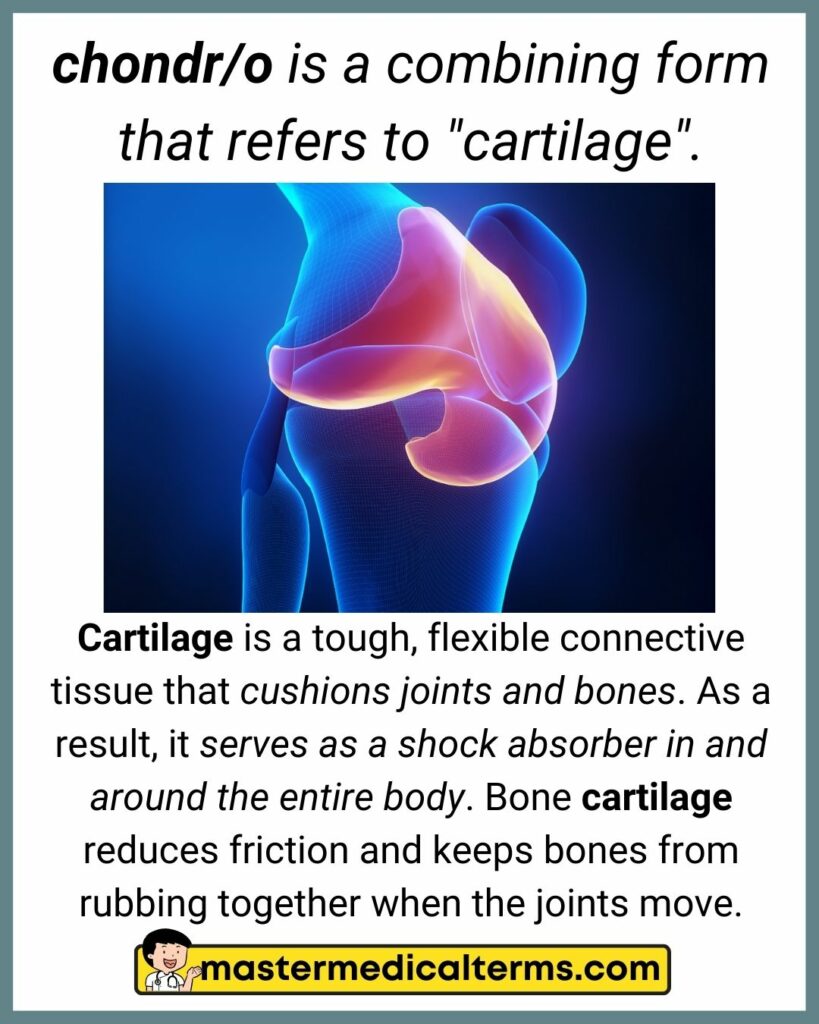
#6 chondr/o
chondr/o is a combining form that refers to "cartilage".
Cartilage is a tough, flexible connective tissue that cushions joints and bones. As a result, it serves as a shock absorber in and around the entire body. Bone cartilage reduces friction and keeps bones from rubbing together when the joints move.
#7 clavic/o, clavicul/o
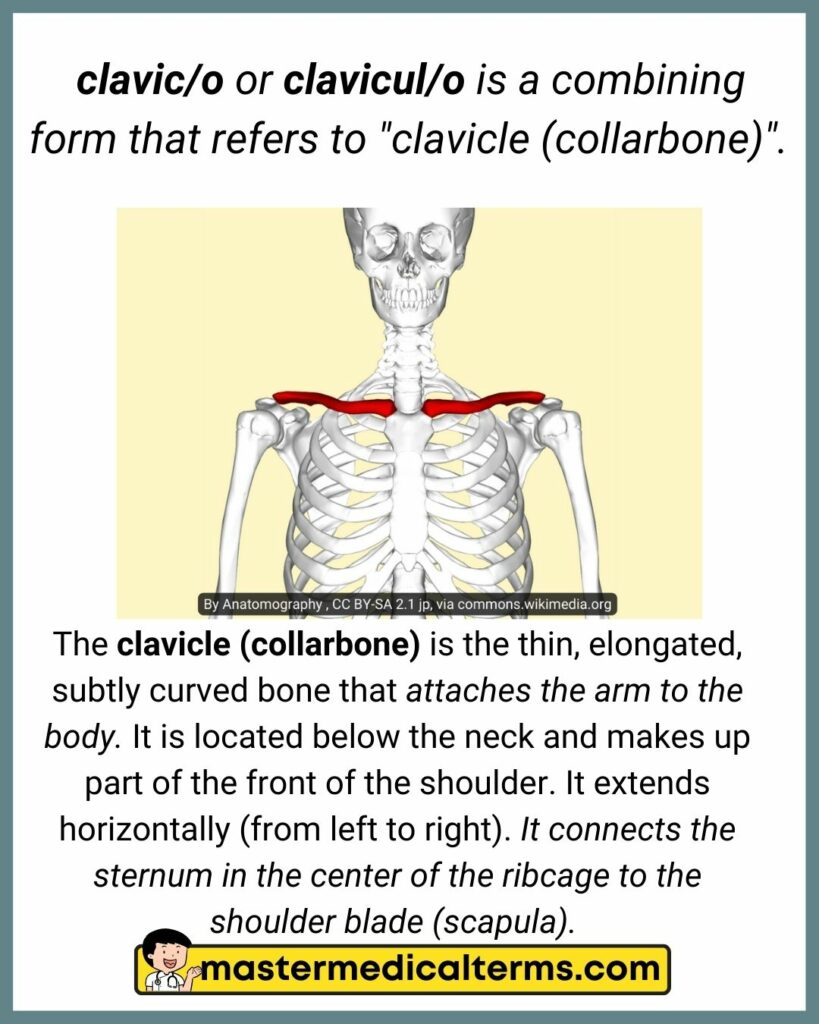
clavic/o or clavicul/o is a combining form that refers to "clavicle (collarbone)".
The clavicle (collarbone) is the thin, elongated, subtly curved bone that attaches the arm to the body. It is located below the neck and makes up part of the front of the shoulder. It extends horizontally (from left to right). It connects the sternum in the center of the ribcage to the shoulder blade (scapula).
#8 coccy, coccyg/o
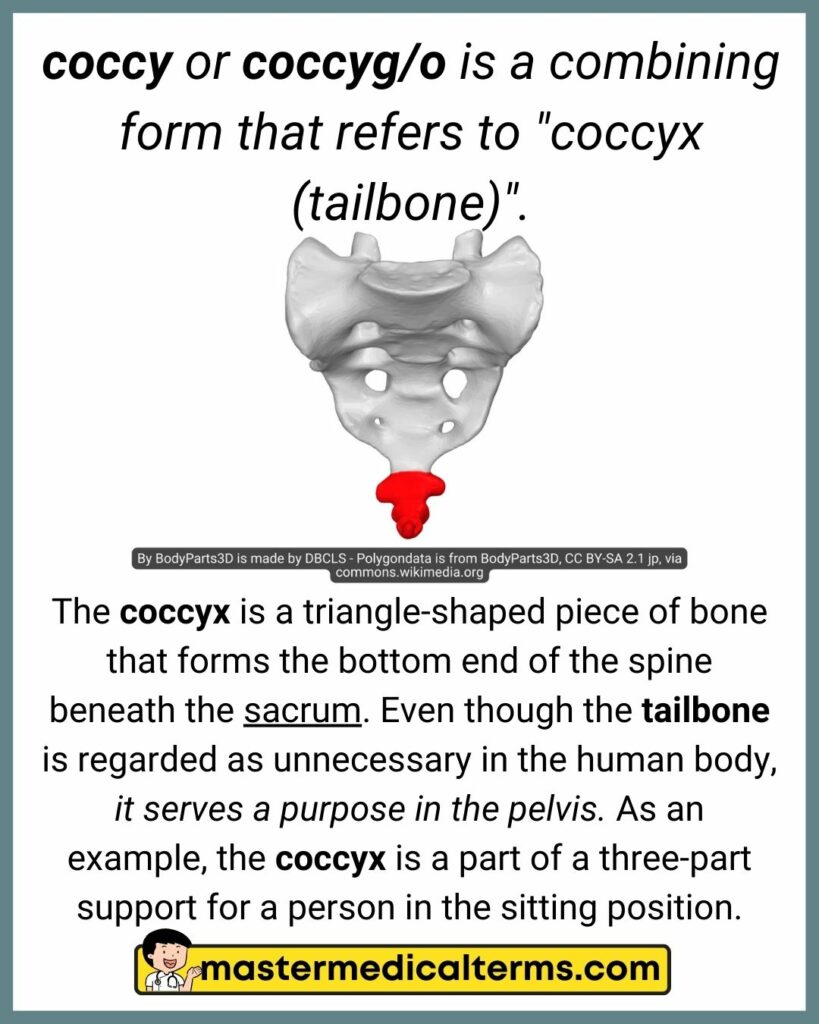
coccy or coccyg/o is a combining form that refers to "coccyx (tailbone)".
The coccyx is a triangle-shaped piece of bone that forms the bottom end of the spine beneath the sacrum. Even though the tailbone is regarded as unnecessary in the human body, it serves a purpose in the pelvis. As an example, the coccyx is a part of a three-part support for a person in the sitting position.
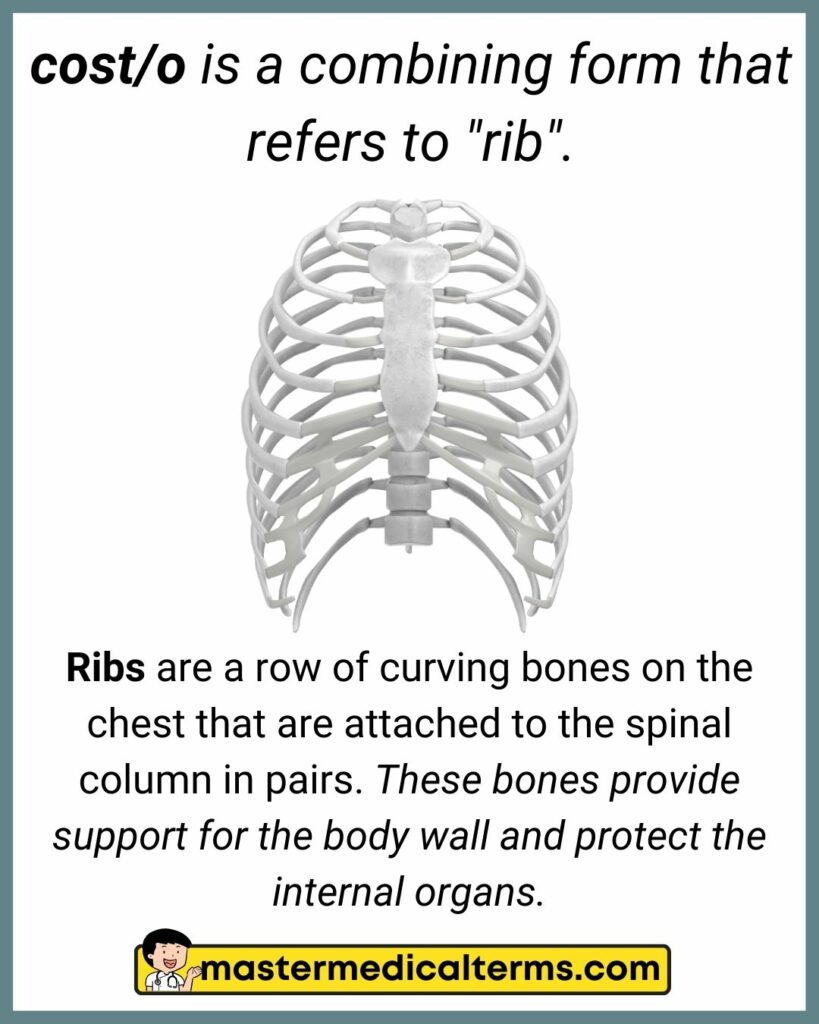
#9 cost/o
#10 crani/o
#11 disk/o
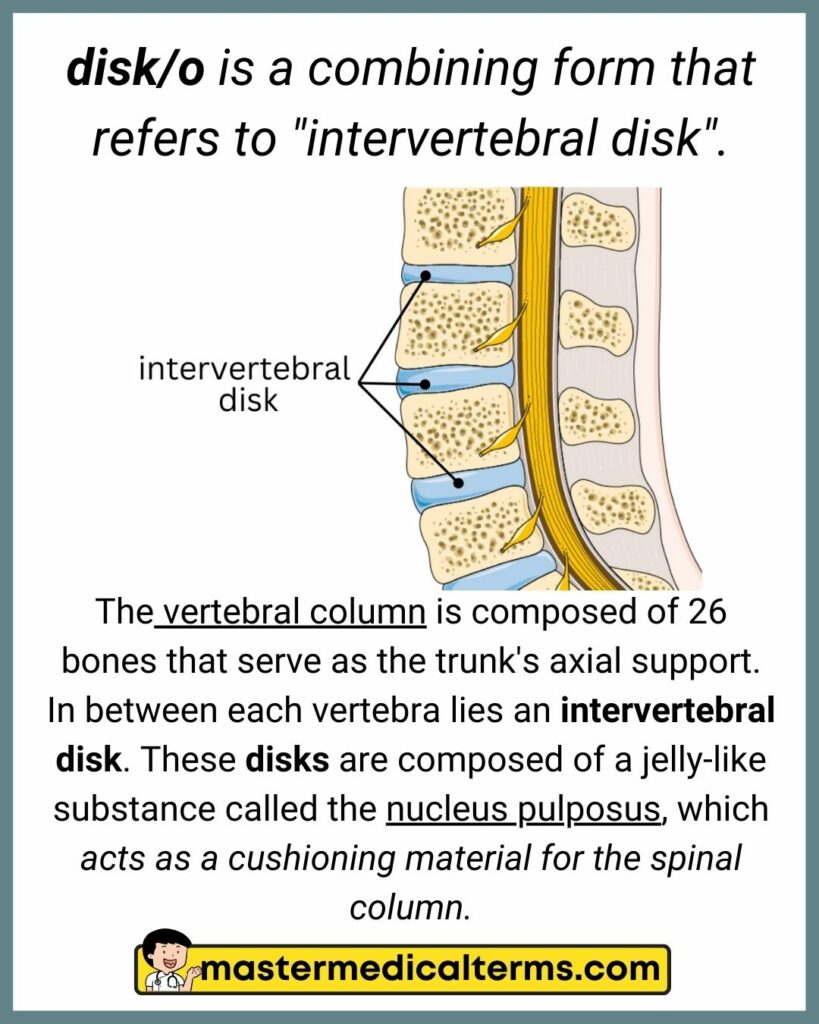
disk/o is a combining form that refers to "intervertebral disk".
The vertebral column is composed of 26 bones that serve as the trunk's axial support. In between each vertebra lies an intervertebral disk. These disks are composed of a jelly-like substance called the nucleus pulposus, which acts as a cushioning material for the spinal column.
#12 femor/o
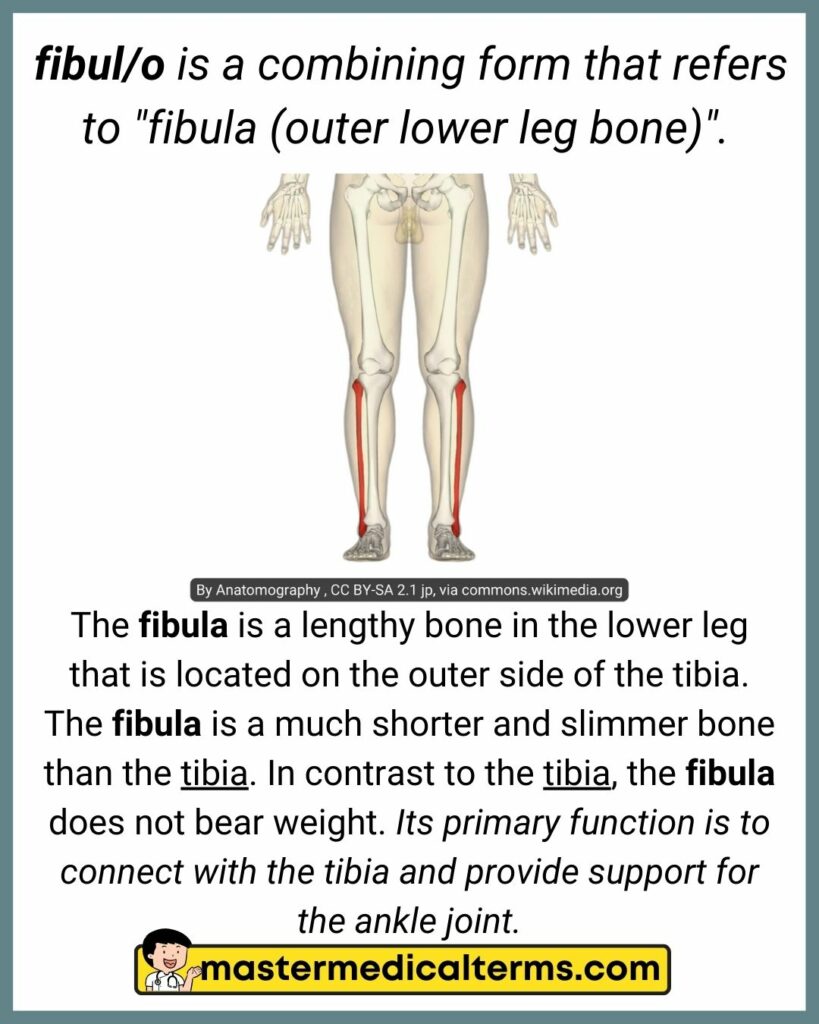
#13 fibul/o
fibul/o is a combining form that refers to "fibula (outer lower leg bone)".
The fibula is a lengthy bone in the lower leg that is located on the outer side of the tibia. The fibula is a much shorter and slimmer bone than the tibia. In contrast to the tibia, the fibula does not bear weight. Its primary function is to connect with the tibia and provide support for the ankle joint.
#14 humer/o
#15 ili/o
ili/o is a combining form that refers to "ilium".
The ilium comprises the upper part of the hip bone and pelvis. This is the largest and topmost bone of the hip and is crucial to the pelvic girdle. The ilium supports the body's weight and forms the structure that makes sure the spine is stable when the body is standing. Therefore, it is crucial as part of the mechanism that facilitates mobility.
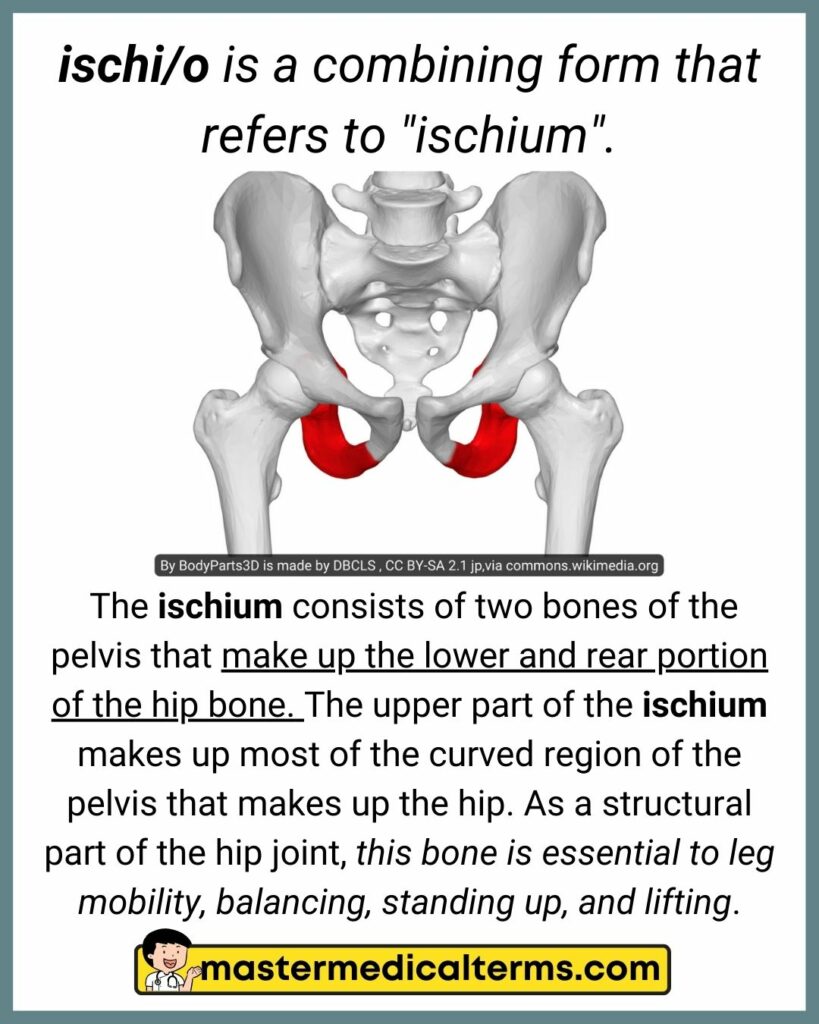
#16 ischi/o
ischi/o is a combining form that refers to "ischium".
The ischium consists of two bones of the pelvis that make up the lower and rear portion of the hip bone. The upper part of the ischium makes up most of the curved region of the pelvis that makes up the hip. As a structural part of the hip joint, this bone is essential to leg mobility, balancing, standing up, and lifting.
#17 kinesi/o
#18 kyph/o
kyph/o is a combining form that refers to "humpback".
Kyphosis, also called roundback, humpback or hunchback, describes an abnormality where the spine in the upper back exhibits too much curve. Having improper posture in childhood, like slouching, slumping back in chairs, and carrying heavy backpacks, puts pressure on the muscles and ligaments in the spine to strain. This causes the vertebrae in the thorax to pull out of place, which results in kyphosis.
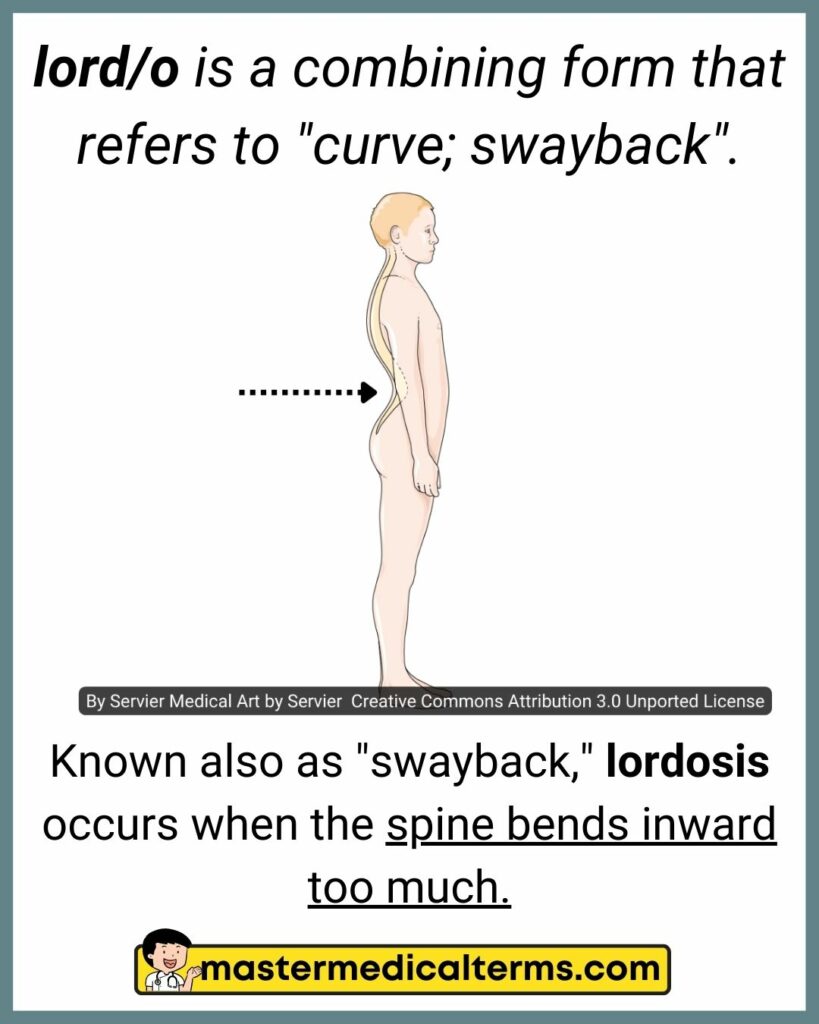
#19 lord/o
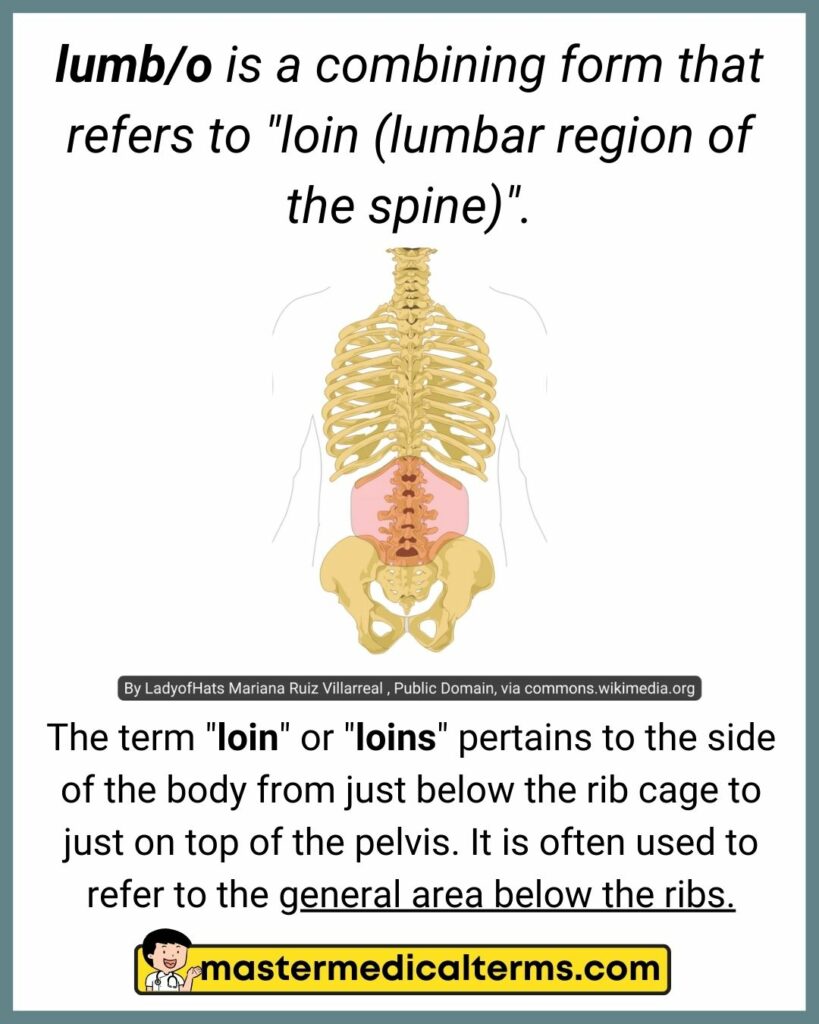
#20 lumb/o
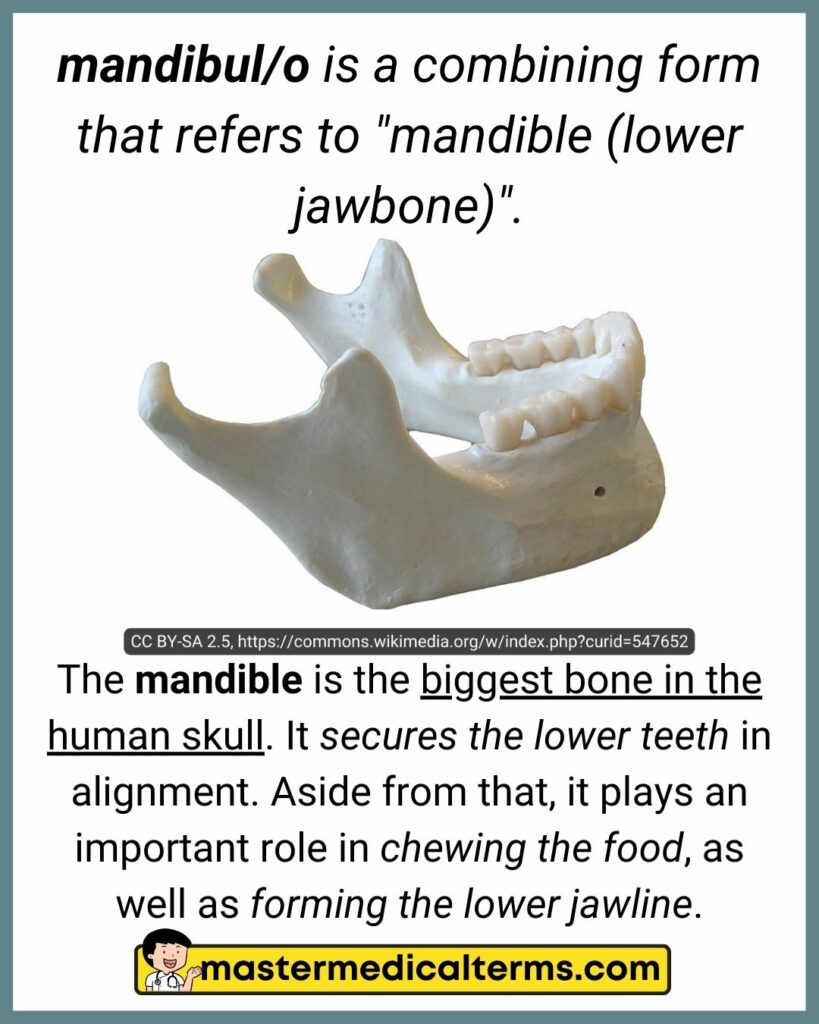
#21 mandibul/o
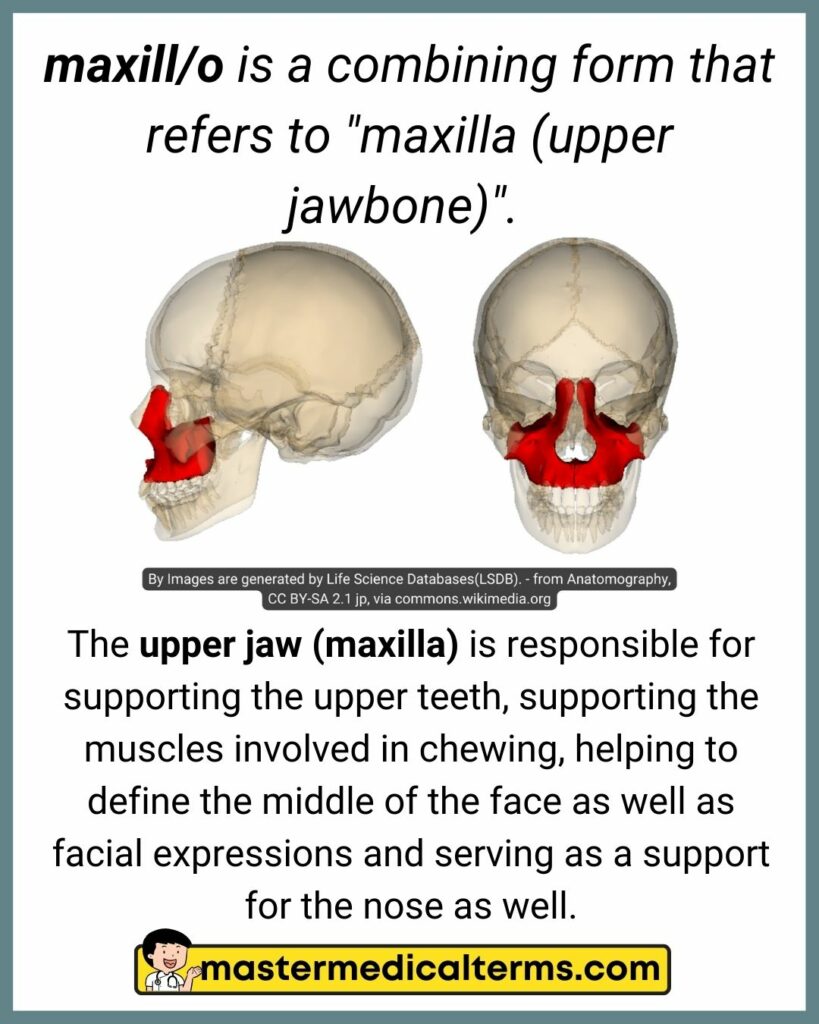
#22 maxill/o
maxill/o is a combining form that refers to "maxilla (upper jawbone)".
The upper jaw (maxilla) is responsible for supporting the upper teeth, supporting the muscles involved in chewing, helping to define the middle of the face as well as facial expressions and serving as a support for the nose as well.
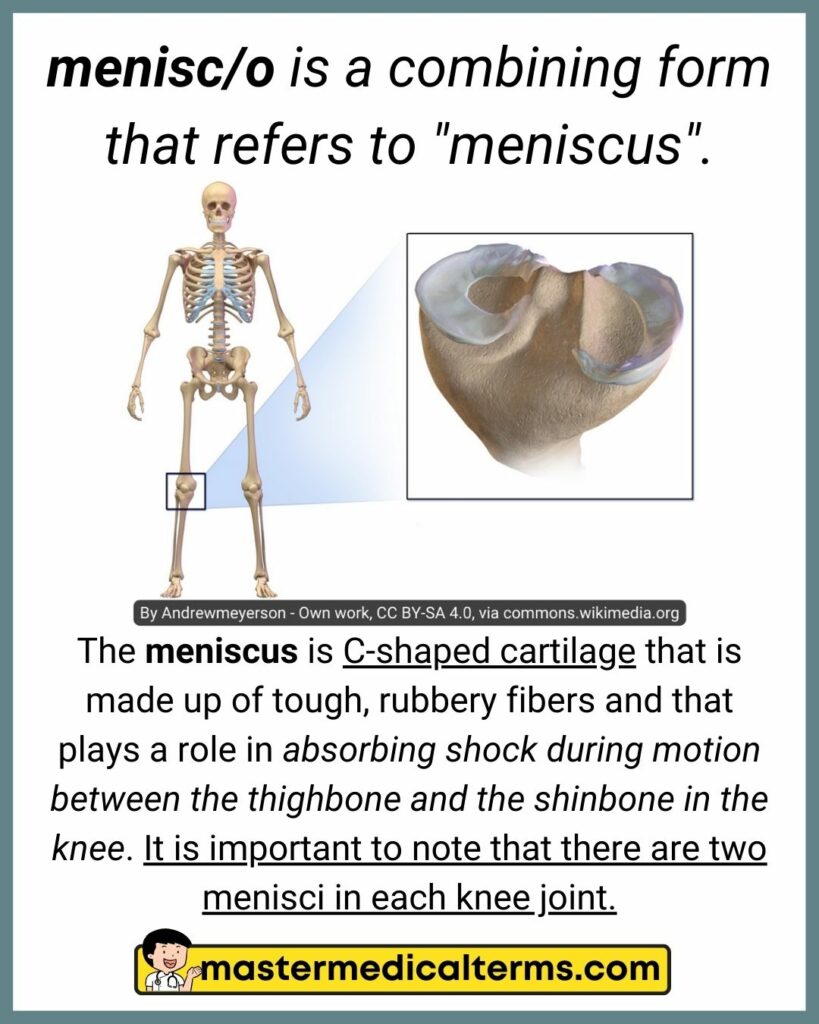
#23 menisc/o
menisc/o is a combining form that refers to "meniscus".
The meniscus is C-shaped cartilage that is made up of tough, rubbery fibers and that plays a role in absorbing shock during motion between the thighbone and the shinbone in the knee. It is important to note that there are two menisci in each knee joint.
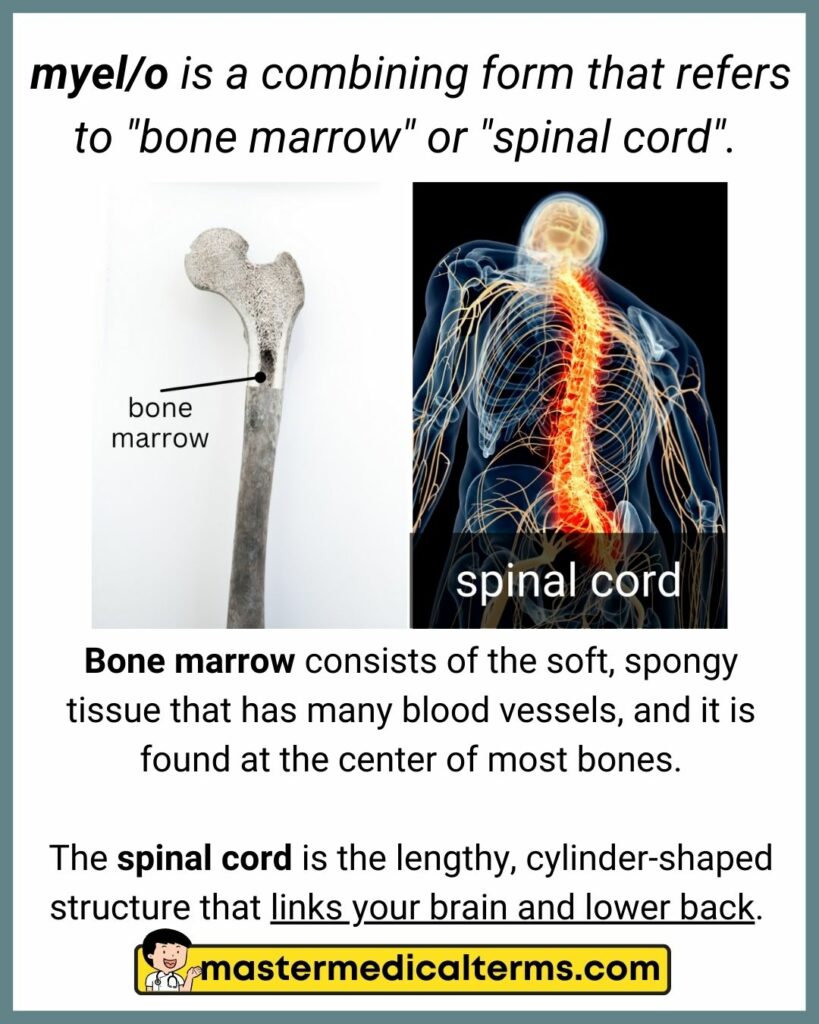
#24 myel/o
myel/o is a combining form that refers to "bone marrow" or "spinal cord".
Bone marrow consists of the soft, spongy tissue that has many blood vessels, and it is found at the center of most bones.
The spinal cord is the lengthy, cylinder-shaped structure that links your brain and lower back.
Examples of Medical Terms Containing myel/o
Myelitis: myel ( "bone marrow" or "spinal cord") + -itis ( "inflammation")
Definition: Inflammation of the spinal cord, which can cause pain, weakness, and difficulty moving.
Myeloid: myel ( "bone marrow" or "spinal cord") + -oid ( "resembling")
Definition: Resembling bone marrow or the cells that form in bone marrow.
Myeloma: myel ( "bone marrow" or "spinal cord") + -oma ( "tumor")
Definition: A type of cancer that begins in the bone marrow and affects the white blood cells.
Myelocyte: myel/o ( "bone marrow" or "spinal cord") + -cyte ( "cell")
Definition: A type of cell found in the bone marrow.
Myelography: myel/o ( "bone marrow" or "spinal cord") + -graphy ( "process of recording")
Definition: A diagnostic procedure that uses X-ray or CT images to visualize the spinal cord and the spaces surrounding it.
Myelopathy: myel/o ( "bone marrow" or "spinal cord") + -pathy ( "disease")
Definition: A disease or disorder of the spinal cord, which can cause pain, weakness, and difficulty moving.
Myelopoiesis: myel/o ( "bone marrow" or "spinal cord") + -poiesis ( "production")
Definition: The production of blood cells in the bone marrow.
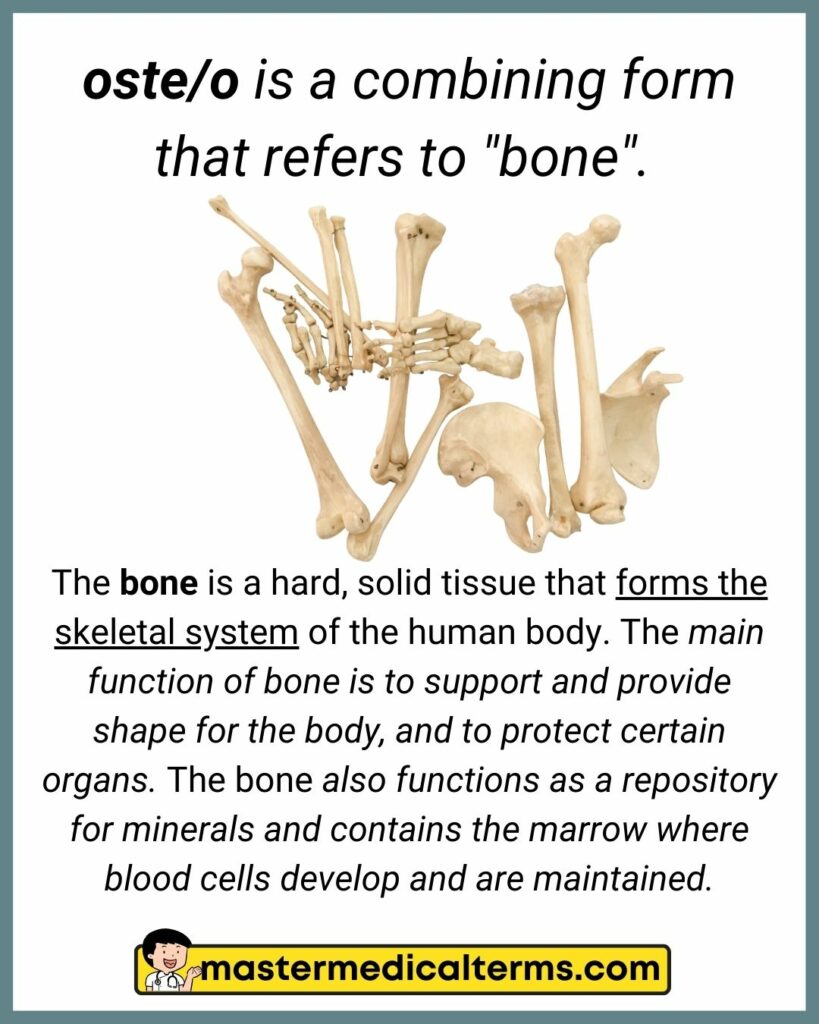
#25 oste/o
oste/o is a combining form that refers to "bone".
The bone is a hard, solid tissue that forms the skeletal system of the human body. The main function of bone is to support and provide shape for the body, and to protect certain organs. The bone also functions as a repository for minerals and contains the marrow where blood cells develop and are maintained.
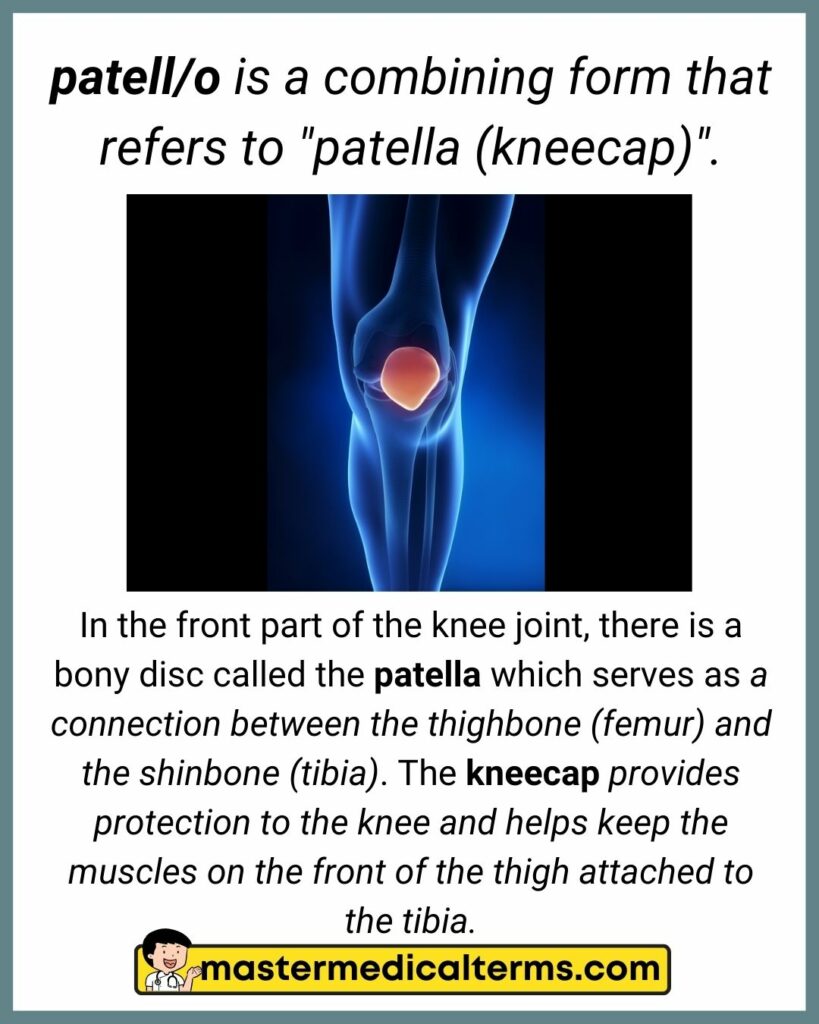
#26 patell/o
patell/o is a combining form that refers to "patella (kneecap)".
In the front part of the knee joint, there is a bony disc called the patella which serves as a connection between the thighbone (femur) and the shinbone (tibia). The kneecap provides protection to the knee and helps keep the muscles on the front of the thigh attached to the tibia.
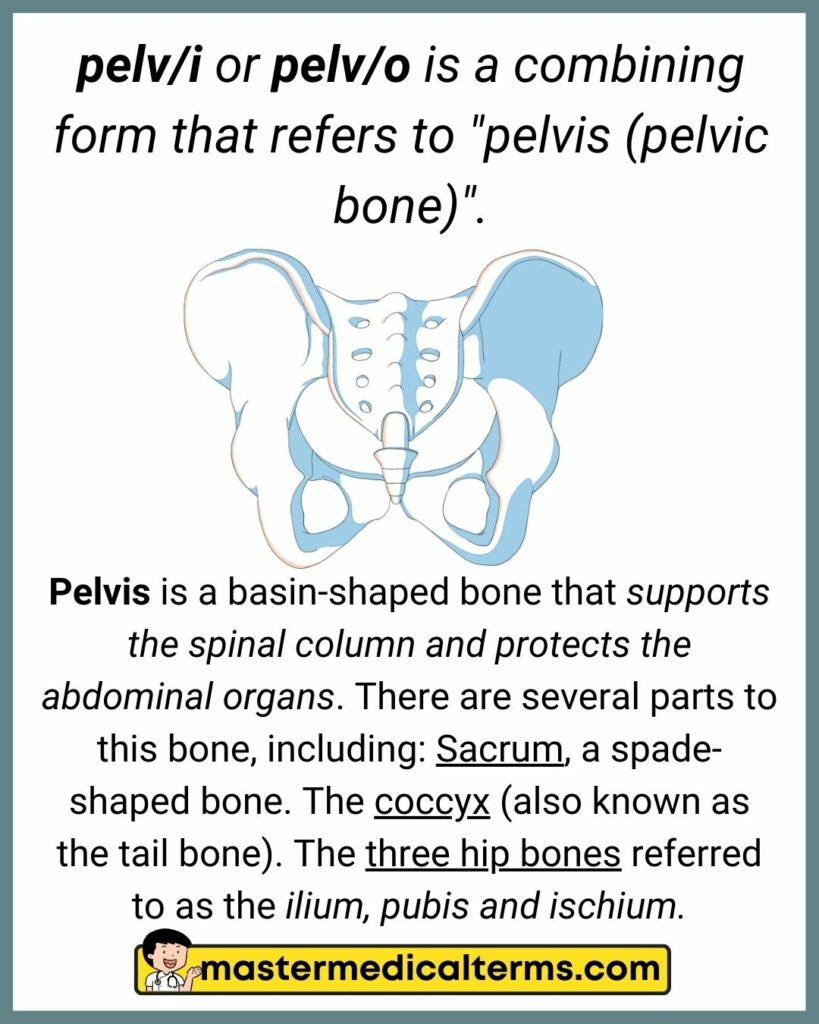
#27 pelv/i, pelv/o
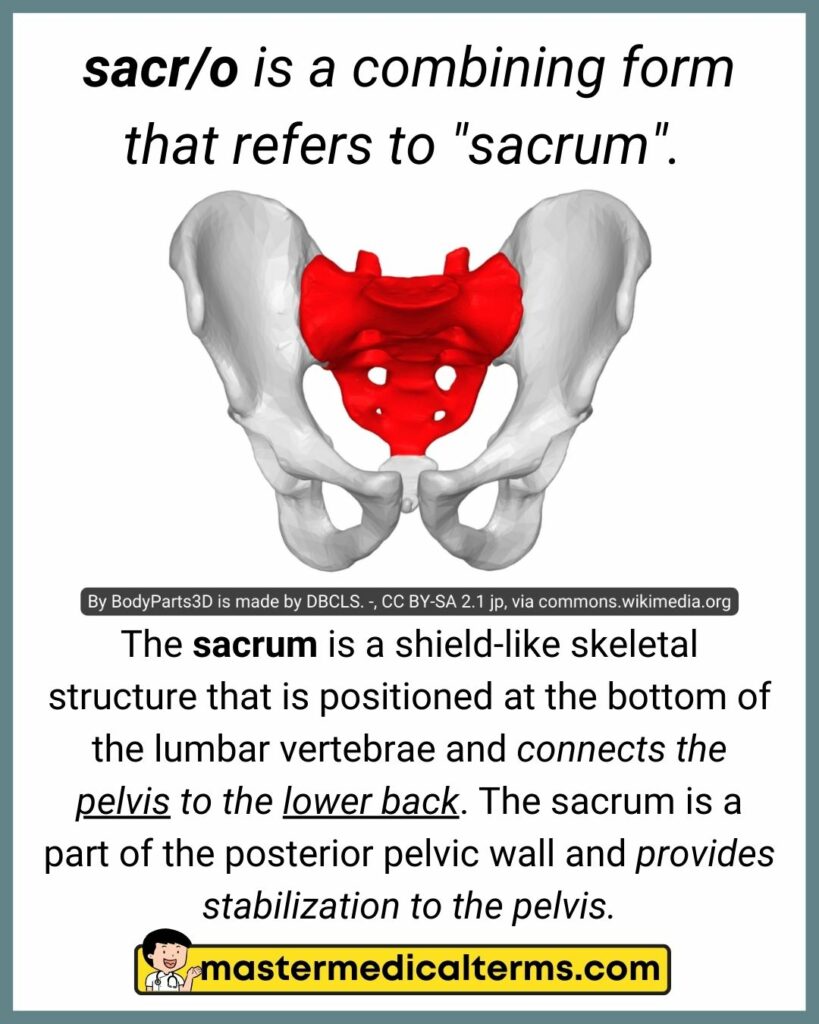
pelv/i or pelv/o is a combining form that refers to "pelvis (pelvic bone)".
Pelvis is a basin-shaped bone that supports the spinal column and protects the abdominal organs. There are several parts to this bone, including: Sacrum, a spade-shaped bone. The coccyx (also known as the tail bone). The three hip bones referred to as the ilium, pubis and ischium.
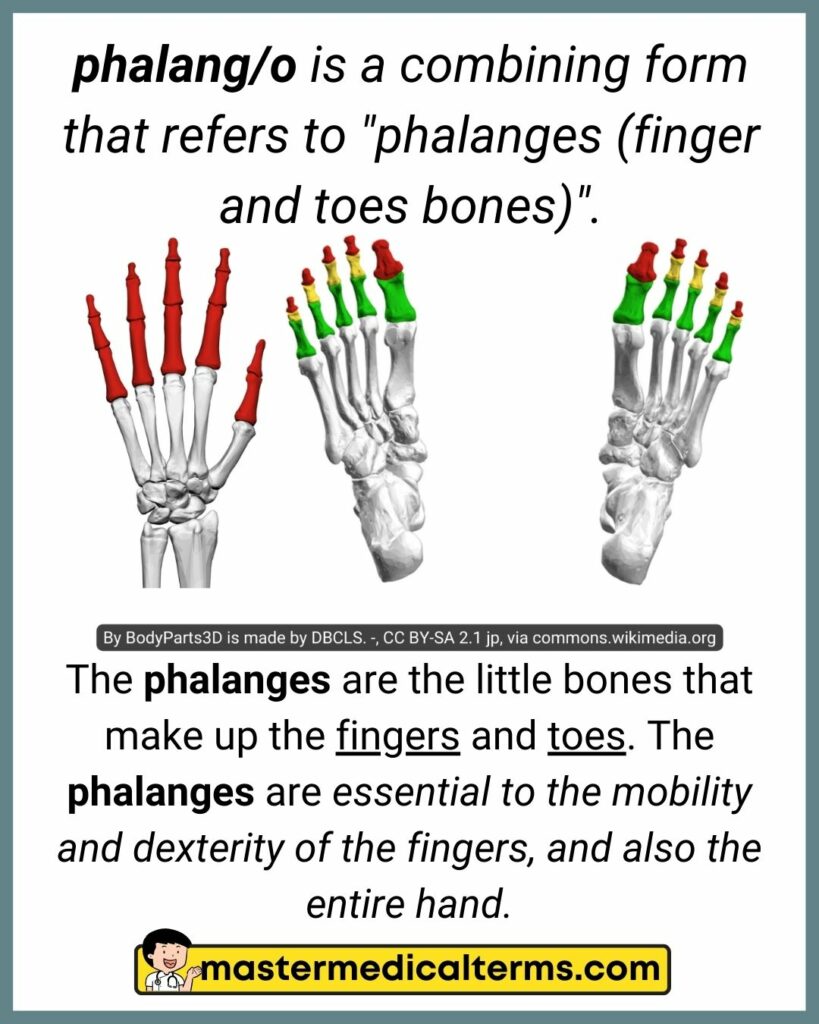
#28 phalang/o
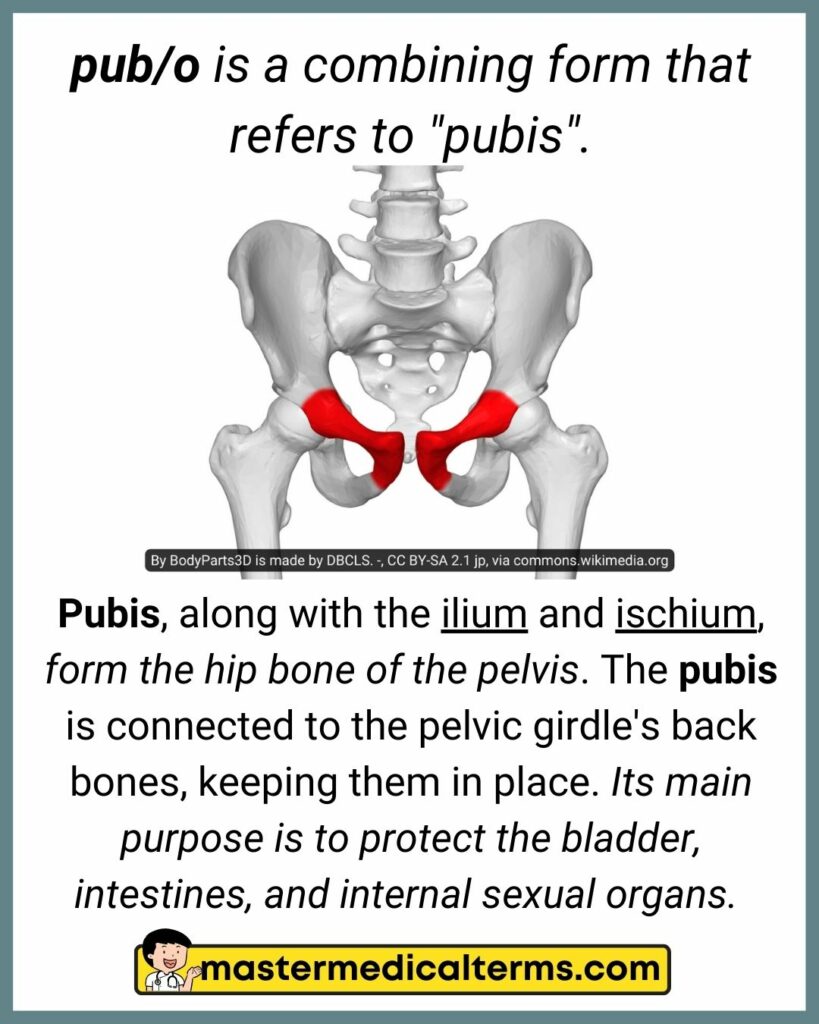
#29 pub/o
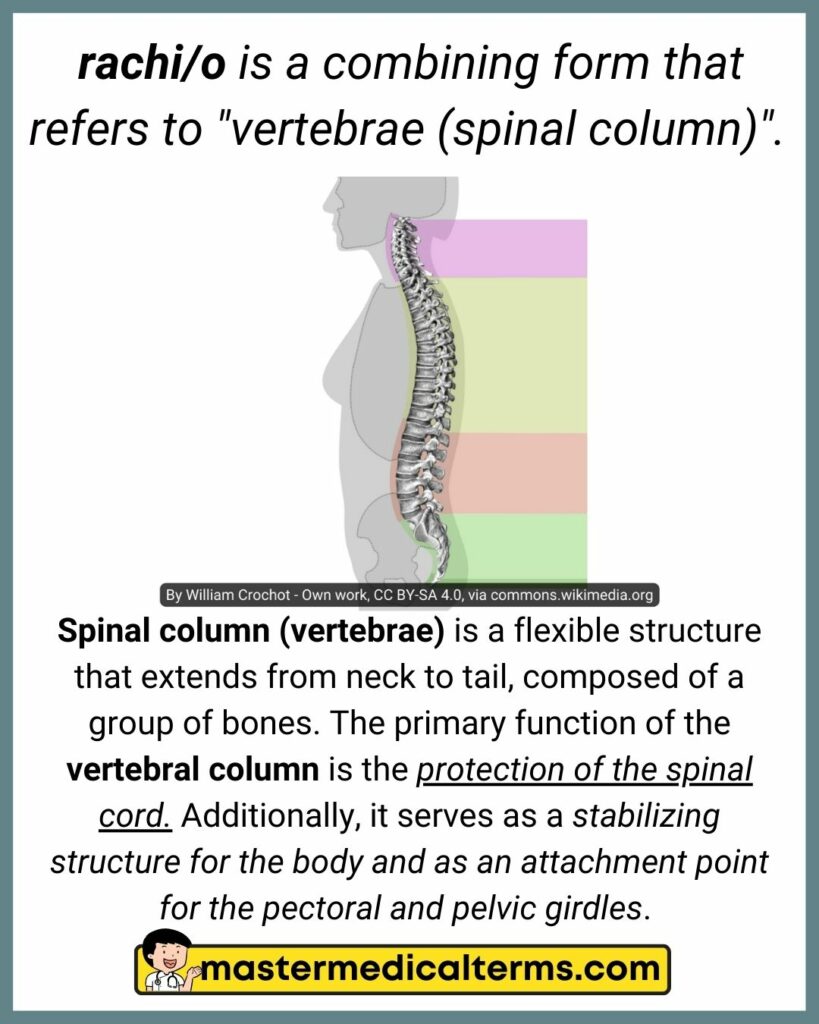
#30 rachi/o
rachi/o is a combining form that refers to "vertebrae (spinal column)".
Spinal column (vertebrae) is a flexible structure that extends from neck to tail, composed of a group of bones. The primary function of the vertebral column is the protection of the spinal cord. Additionally, it serves as a stabilizing structure for the body and as an attachment point for the pectoral and pelvic girdles.
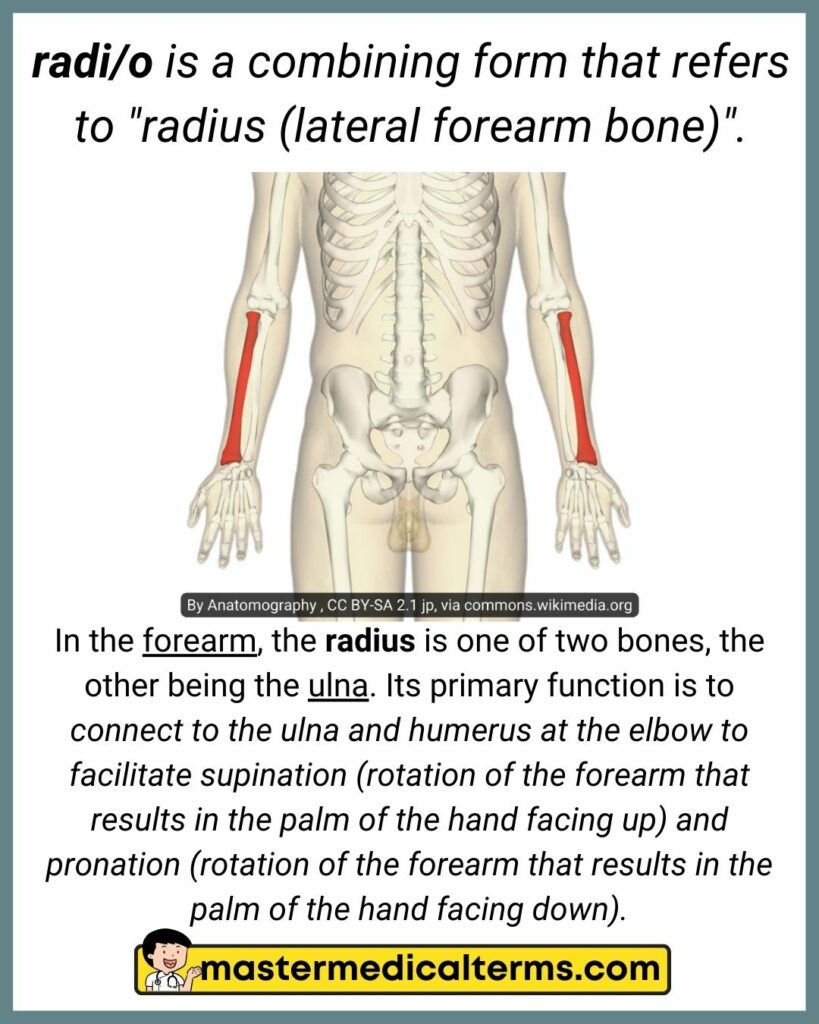
#31 radi/o
radi/o is a combining form that refers to "radius (lateral forearm bone)".
In the forearm, the radius is one of two bones, the other being the ulna. Its primary function is to connect to the ulna and humerus at the elbow to facilitate supination (rotation of the forearm that results in the palm of the hand facing up) and pronation (rotation of the forearm that results in the palm of the hand facing down).
#32 sacr/o
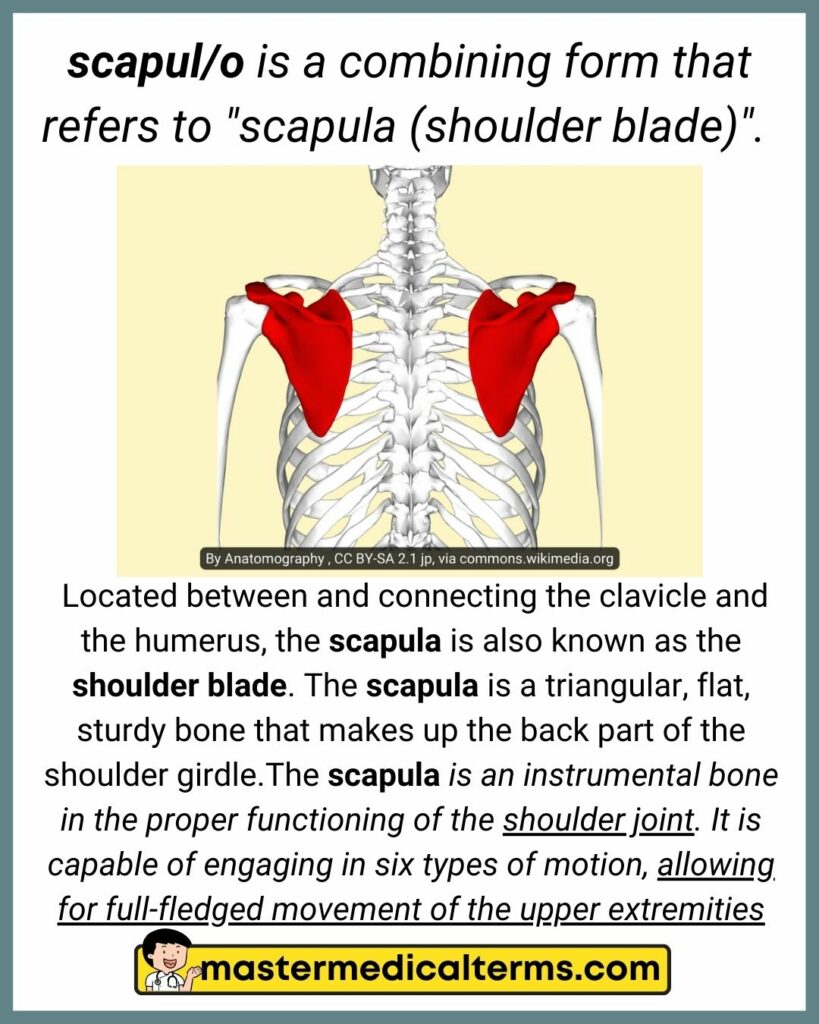
#33 scapul/o
scapul/o is a combining form that refers to "scapula (shoulder blade)".
Located between and connecting the clavicle and the humerus, the scapula is also known as the shoulder blade. The scapula is a triangular, flat, sturdy bone that makes up the back part of the shoulder girdle.The scapula is an instrumental bone in the proper functioning of the shoulder joint. It is capable of engaging in six types of motion, allowing for full-fledged movement of the upper extremities
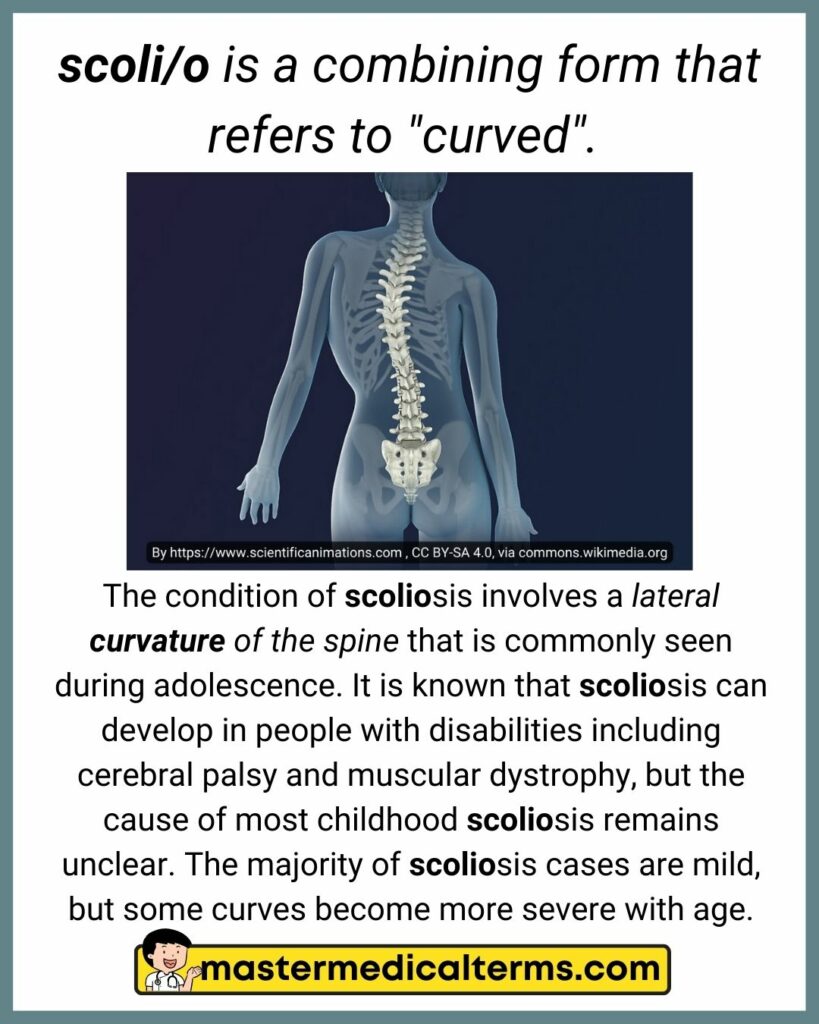
#34 scoli/o
scoli/o is a combining form that refers to "curved".
The condition of scoliosis involves a lateral curvature of the spine that is commonly seen during adolescence. It is known that scoliosis can develop in people with disabilities including cerebral palsy and muscular dystrophy, but the cause of most childhood scoliosis remains unclear. The majority of scoliosis cases are mild, but some curves become more severe with age.
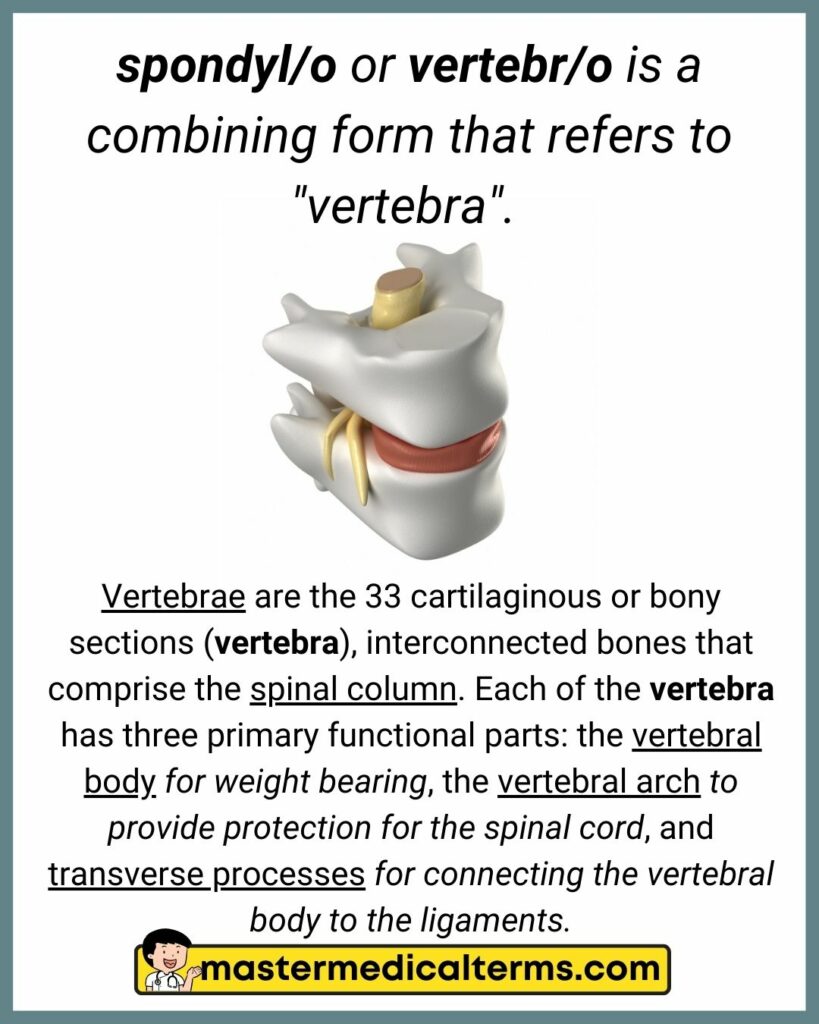
#35 spondyl/o, vertebr/o
spondyl/o or vertebr/o is a combining form that refers to "vertebra".
Vertebrae are the 33 cartilaginous or bony sections (vertebra), interconnected bones that comprise the spinal column. Each of the vertebra has three primary functional parts: the vertebral body for weight bearing, the vertebral arch to provide protection for the spinal cord, and transverse processes for connecting the vertebral body to the ligaments.
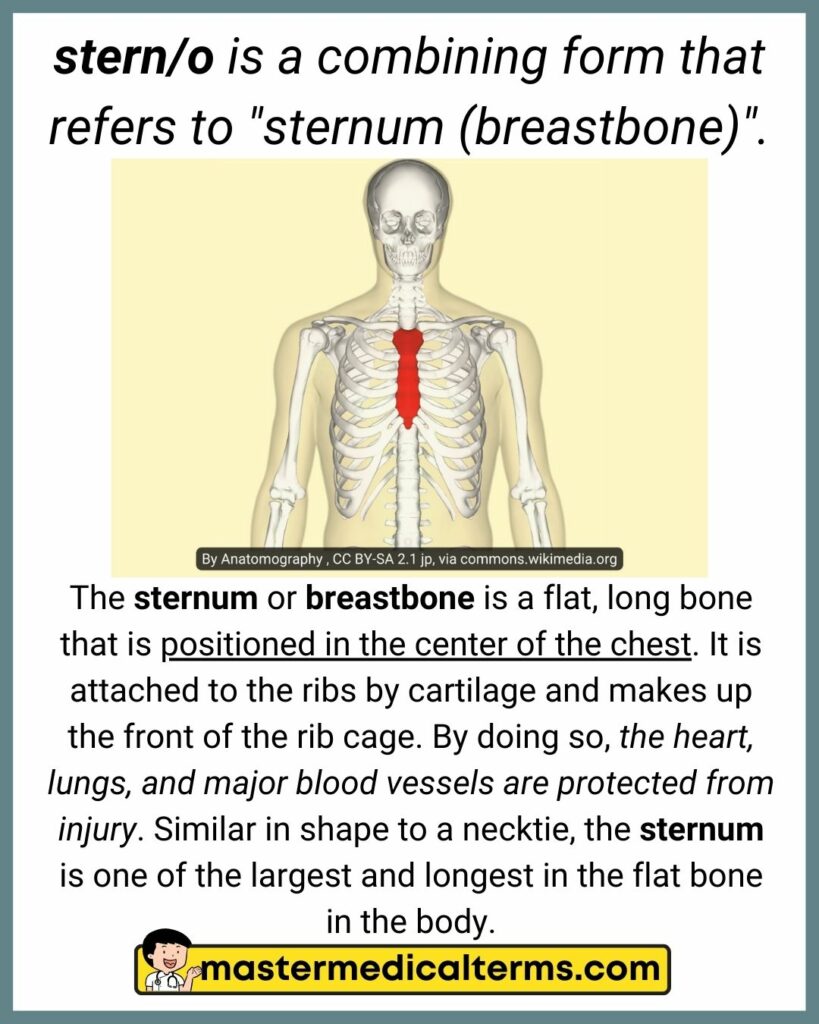
#36 stern/o
stern/o is a combining form that refers to "sternum (breastbone)".
The sternum or breastbone is a flat, long bone that is positioned in the center of the chest. It is attached to the ribs by cartilage and makes up the front of the rib cage. By doing so, the heart, lungs, and major blood vessels are protected from injury. Similar in shape to a necktie, the sternum is one of the largest and longest in the flat bone in the body.
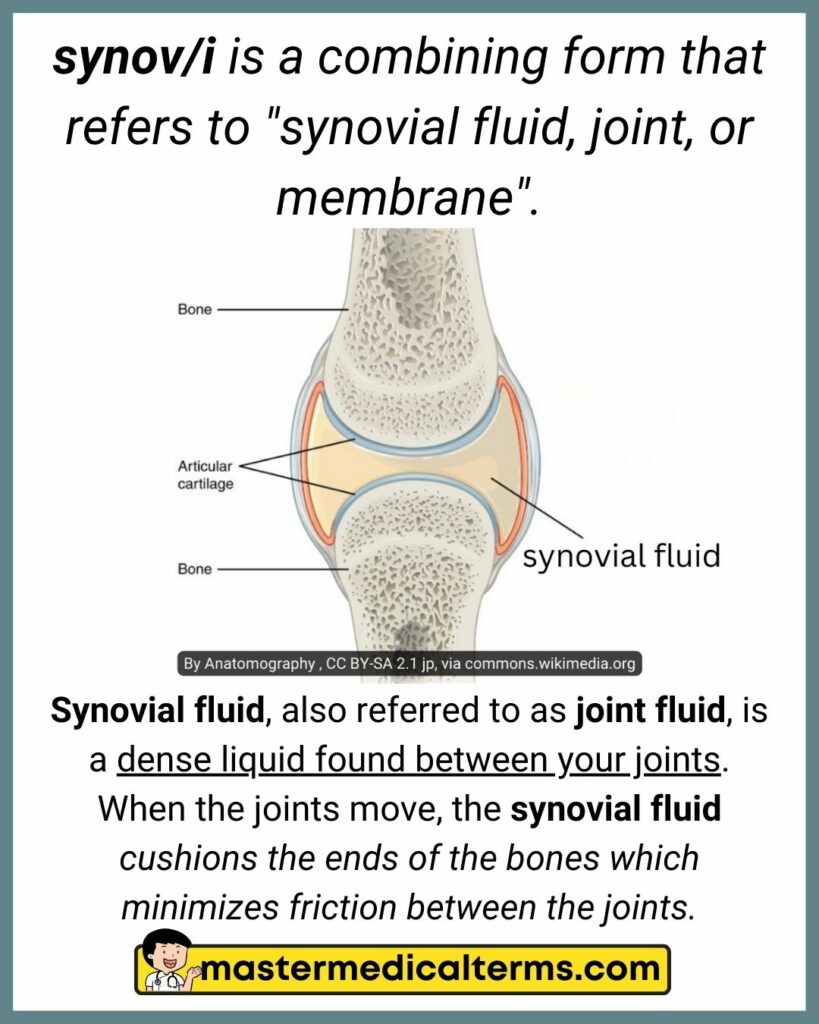
#37 synov/i
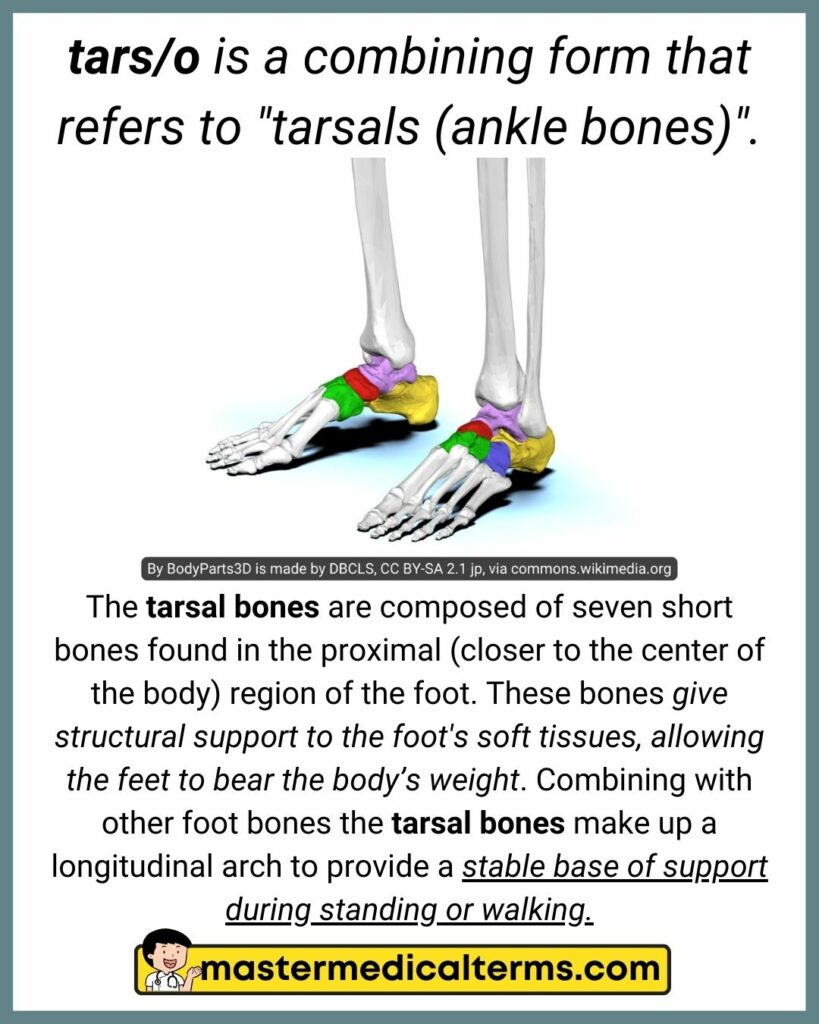
#38 tars/o
tars/o is a combining form that refers to "tarsals (ankle bones)".
The tarsal bones are composed of seven short bones found in the proximal (closer to the center of the body) region of the foot. These bones give structural support to the foot's soft tissues, allowing the feet to bear the body’s weight. Combining with other foot bones the tarsal bones make up a longitudinal arch to provide a stable base of support during standing or walking.
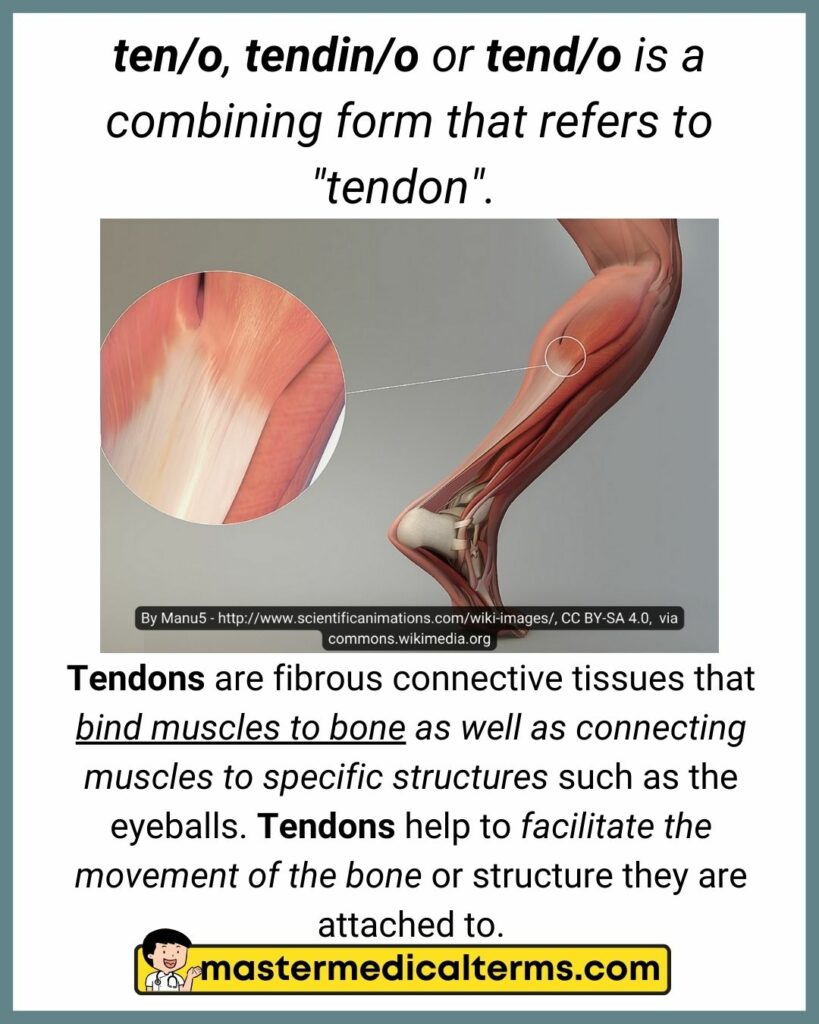
#39 ten/o, tendin/o, tend/o
#40 tibi/o
tibi/o is a combining form that refers to "tibia (inner lower leg bone)".
The tibia, also called the shin bone, is the larger of the two bones in the lower leg. Fibula (calf bone) is another bone in the lower leg. A tibia is located closer to the center of your body (medial) than a fibula, extending from beneath the knee to the ankle. The tibia is the second biggest bone in the body and one of the main bones that bear the weight of the body when it stands and moves.
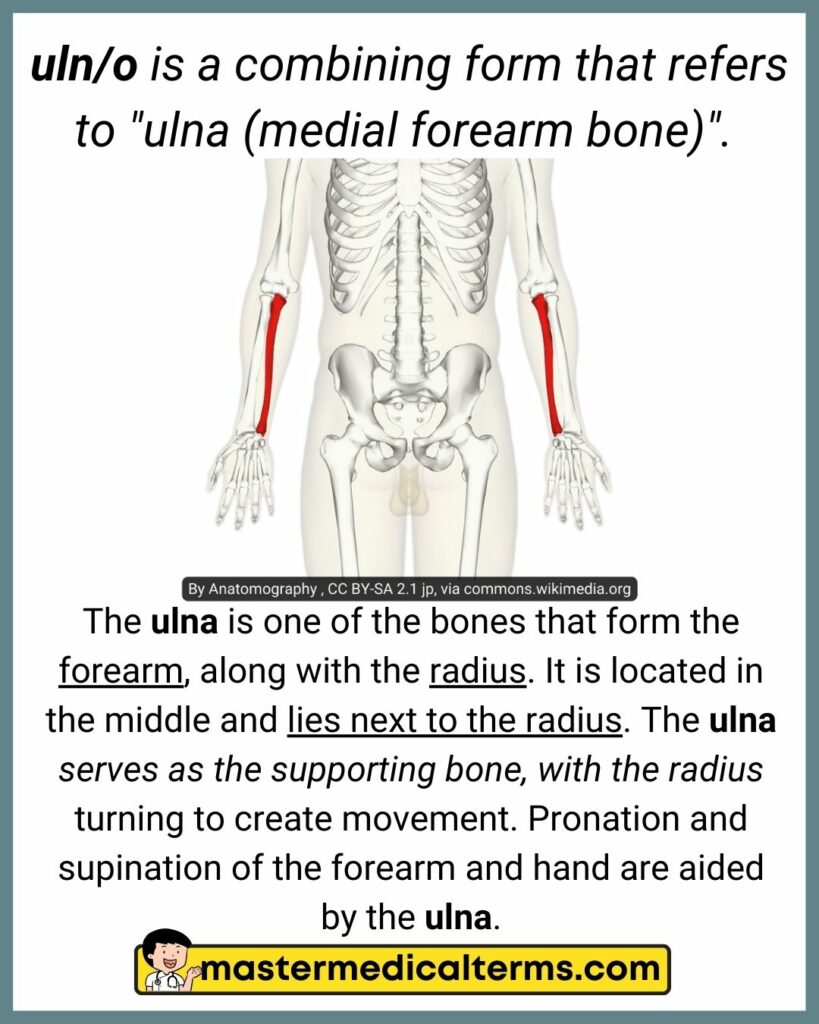
#41 uln/o
uln/o is a combining form that refers to "ulna (medial forearm bone)".
The ulna is one of the bones that form the forearm, along with the radius. It is located in the middle and lies next to the radius. The ulna serves as the supporting bone, with the radius turning to create movement. Pronation and supination of the forearm and hand are aided by the ulna.