Medical terminology is the language of medicine, it is a way of describing the human body and its components, processes, conditions, and procedures. It is based on the terminology of Greek and Latin, it is uniform throughout the world. Medical terminology is vast and mastering it can be like learning an entire foreign language.
Learning Medical Terminology can be a daunting task, but there are ways to remember these medical words and can help in making informed guesses. Medical terms can be divided into root words, prefixes and suffixes. Each retains its meaning when appearing as part of a medical term. By knowing the component parts of medical terms, you can remember many medical words.
What is the purpose of Medical Terminology?
A medical terminology system is a way to create a common language for medical professionals. This language helps medical staff communicate more effectively and it makes documentation easier.
Medical terminology allows medical professionals to communicate more easily with each other, and with other medical professionals allowing them to be more effective in their practice.
When is Medical Terminology used?
Medical terminology is used across the healthcare industry. Medical care is documented using it to ensure that every medical decision and procedures is documented for physicians, nurses, and other medical professionals to collaborate effectively about medical issues.
Medications uses medical terms as well with other variety of medical settings, such as in patient care, lab tests, and more.
Who needs to learn Medical Terminology?
Medical terminology is essential for anyone who works in an environment where a basic understanding of medical terms is required.
Along with some popular healthcare professionals, such as doctors, nurses, radiologists, and pharmacists. The knowledge of medical terminologies is also required for health care assistants, medical transcriptionists, medical records clerks, medical coders, and billers.
Why is it important for health professionals to use Medical Terminology?
Doctors and other health professionals are expected to communicate frequently, so they need to become familiar with medical terms. Medications, procedures, treatments, and medical conditions are often described using medical terms.
Healthcare professionals need to understand medical terms so that they can convey accurate information to patients as well.
Without medical terminology, doctors, nurses, and other healthcare providers would be at risk of misdiagnosing or prescribing the wrong medication. Also, they would make mistakes during medical procedures and health care related procedures.
Medical terminology is the language of medicine. It is the foundation of any successful healthcare profession.
Basic Structure of Medical Terminology
Medical terms are made up of word parts. Prefix, word root, suffix, and combining form vowel are these word parts.
Word Parts
- The prefix is a word part added to the beginning of a medical term that alters the meaning of the root. The prefix usually indicates direction, type, location, quality, or quantity.
- The word root (also known as the root) is the fundamental unit of every medical term. It identifies a word’s basic meaning and is the part to which modifying prefixes and suffixes are added.
- The suffix is a word part that is added to the end of a word root that changes it’s meaning.
- Combining forms vowels are used to connect word parts and to make pronunciation easier. In most cases, combining form vowels are an “o,” but sometimes they are “i” or “e.”
You can identify the meaning of medical terms or words by breaking them down into word parts. Here is an example of the medical word broken down into its parts.
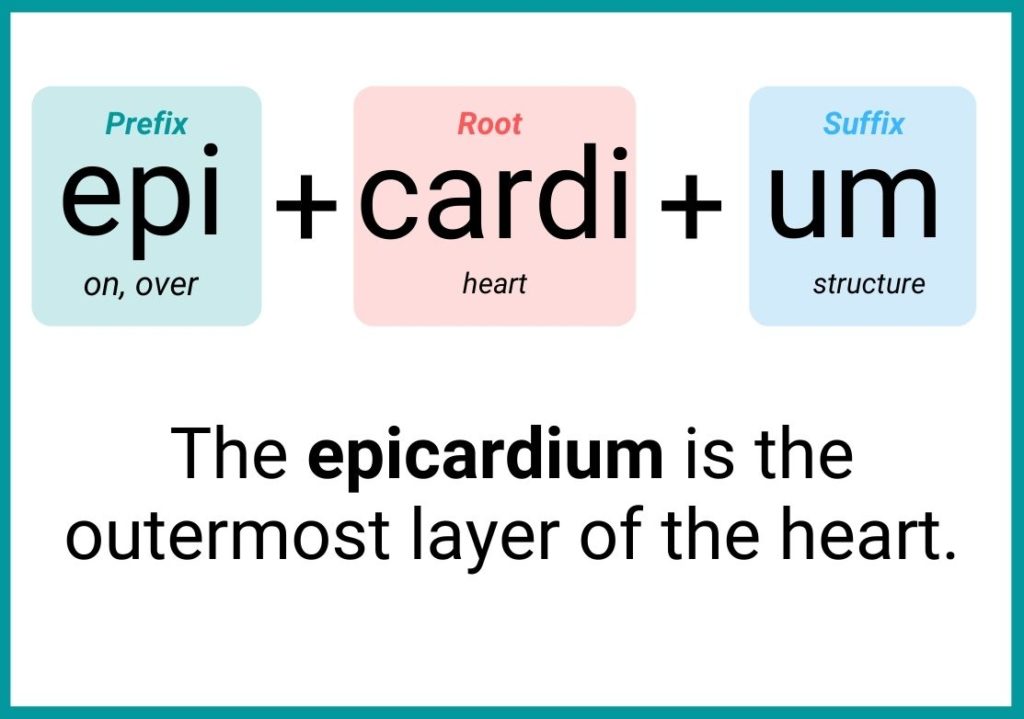
Word Root
The Word Root is the foundational meaning of a medical term. Roots contain the essence of the word, and they are the part to which prefixes and suffixes are added for modifying meanings. Word roots for medical terms often describe an organ, tissue, or condition. Almost every medical term has one or more word roots.
Hypotension, for example, has the prefix “hypo-” meaning “low” or “below”, and the root word “tension” means “pressure”, so the word “hypotension” denotes abnormally low blood pressure.
Combining Form
In order to facilitate pronunciation, a vowel (mostly a letter o) is usually inserted between the root and the suffix when a suffix begins with a consonant.
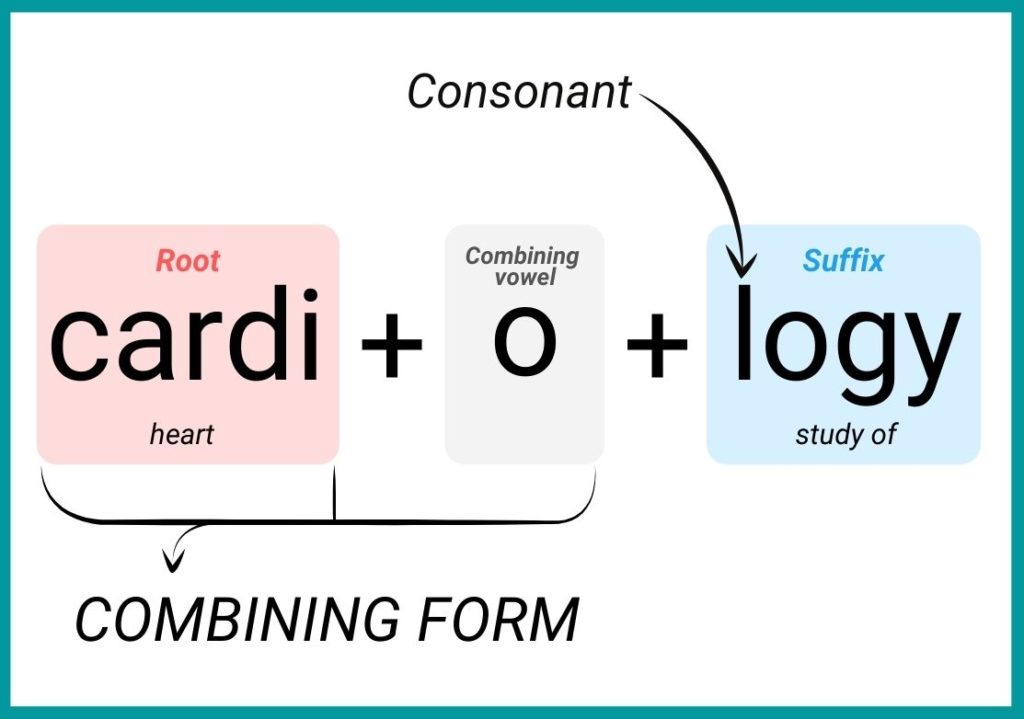
The word part resulting from the combination of a root and a combining form vowel is an example of a combining form. In textbooks, you will notice that combining forms show a slash between the root and the vowel, as in cardi/o.
Basically, combining forms are the combination of word roots + combining form vowels. Simply put, combining form is also a root word that has a combining form vowel on it.
*Most textbooks automatically call Combining Form a Word Root as well.
Compound Words
A compound word is a medical term with multiple roots. This is often the case when referring to more than one body part or system.
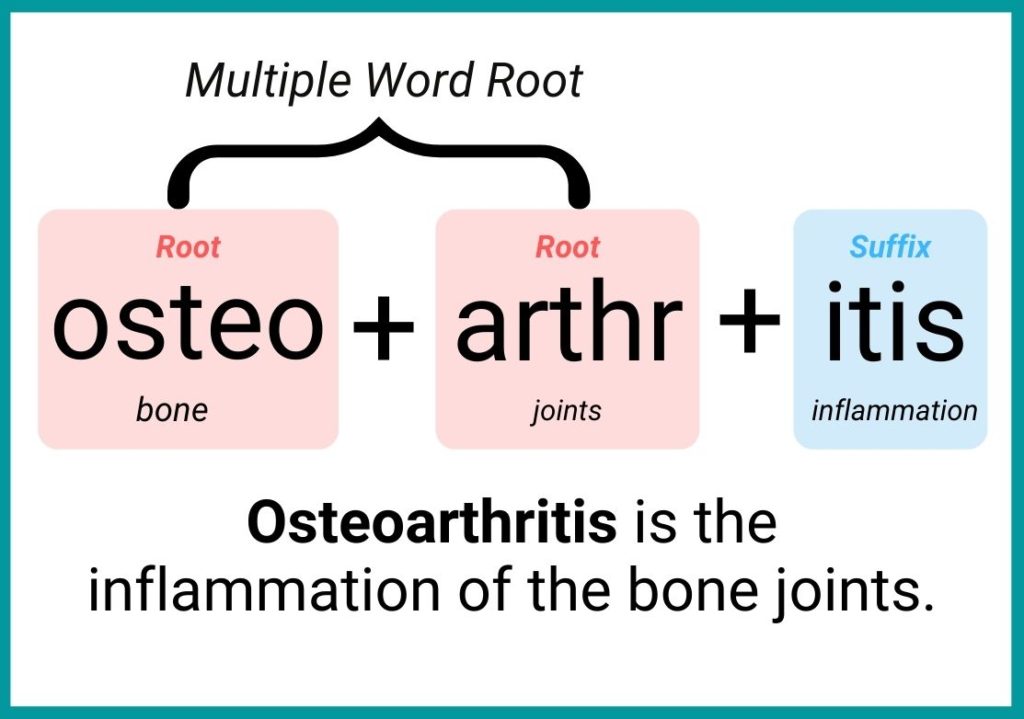
Common Word Roots
Below are lists of common word roots categorized by each system.
Common Word Roots for Cells & Tissues
| Word Root | Combining Form | Body Part or Condition |
|---|---|---|
| aden | aden/o | gland |
| cyt | cyt/o | cell |
| fibr | fibr/o | fiber |
| hist, histi | hist/o, histi/o | tissue |
| morph | morph/o | form |
| myx, muc | myx/o, muc/o | mucus |
| nucle, kary | nucle/o, kary/o | nucleus |
| papill | papill/o | nipple |
| reticul | reticul/o | network |
| somat | somat/o | body |
Here are the more detailed review flashcards for this topic.
💡 Practice Quiz
Common Word Roots for Disease
| Word Root | Combining Form | Body Part or Condition |
|---|---|---|
| alg, algi, algesi | alg/o, algi/o, algesi/o | pain |
| carcin | carcin/o | cancer |
| lith | lith/o | stone |
| onc | onc/o | tumor |
| path | path/o | disease |
| py | py/o | pus |
| pyr, pyret | pyr/o, pyret/o | fever |
| therm | therm/o | heat |
| tox, toxic | tox/o, toxic/o | poison or toxin |
Here are the more detailed review flashcards for this topic.
💡 Practice Quiz
Common Word Roots for Cardiovascular System
| Word Root | Combining Form | Body Part or Condition |
|---|---|---|
| angi, vas, vascul | angi/o, vas/o, vascul/o | vessel (usually blood vessel) |
| aort | aort/o | aorta |
| arter, arteri | arter/o, arteri/o | artery |
| arteriol | arteriol/o | arteriole |
| ather | ather/o | fatty plaque |
| atri | atri/o | atrium |
| cardi | cardi/o | heart |
| hemat, hem | hemat/o, hem/o | blood |
| isch | isch/o | blockage |
| myel | myel/o | bone marrow (also refers to spinal cord) |
| plasm | plasm/o | plasma |
| thromb | thromb/o | clot |
| valv, valvul | valv/o, valvul/o | valve |
| ven, ven, phleb | ven/o, ven/i, phleb/o | vein |
| ventricul | ventricul/o | ventricle |
Here are the more detailed review flashcards for this topic.
💡 Practice Quiz
Common Word Roots for Lymphatic System
| Word Root | Combining Form | Body Part or Condition |
|---|---|---|
| adenoid | adenoid/o | adenoids |
| immun | immun/o | immune or immunity |
| lymph | lymph/o | lymph or lymphatic system |
| lymphaden | lymphaden/o | lymph gland or lymph node |
| lymphangi | lymphangi/o | lymphatic vessel |
| myel | myel/o | bone marrow (also refers to spinal cord) |
| splen | splen/o | spleen |
| thym | thym/o | thymus gland |
| tonsill | tonsill/o | tonsil |
Here are the more detailed review flashcards for this topic.
💡 Practice Quiz
Common Word Roots for Respiratory System
| Word Root | Combining Form | Body Part or Condition |
|---|---|---|
| alveol | alveol/o | alveolus |
| bronch, bronch, bronchi | bronch/o, bronch/i, bronchi/o | bronchus, bronchial tube |
| bronchiol | bronchiol/o | bronchiole |
| capn | capn/o | carbon dioxide |
| epiglott | epiglott/o | epiglottis |
| laryng | laryng/o | larynx |
| lob | lob/o | lobe |
| muc | muc/o | mucus |
| nas, rhin | nas/o, rhin/o | nose |
| ox | ox/i | oxygen |
| pharyng | pharyng/o | pharynx |
| phon, son | phon/o, son/o | sound, voice |
| phren, diaphragmat | phren/o, diaphragmat/o | diaphragm |
| phrenic | phrenic/o | phrenic nerve |
| pleur | pleur/o | pleura |
| pulm, pulmon, pneumon, pneum, pneumat | pulm/o, pulmon/o, pneumon/o, pneum/o, pneumat/o | lungs or respiration |
| py | py/o | pus |
| radi | radi/o | x-rays or ionizing radiation |
| sept | sept/o | septum |
| sinus | sinus/o | sinus |
| spir, respir | spir/o, respir/o | breathing |
| thorac | thorac/o | thorax or chest cavity |
| trache | trache/o | trachea |
Here are the more detailed review flashcards for this topic.
💡 Practice Quiz
- Common Word Roots for Respiratory System (Part 1) [Practice Quiz]
- Common Word Roots for Respiratory System (Part 2) [Practice Quiz]
Common Word Roots for Digestive System
| Word Root | Combining Form | Body Part or Condition |
|---|---|---|
| abdomin , celi, lapar | abdomin/o , celi/o, lapar/o | abdomen or abdominal |
| an | an/o | anus |
| antr | antr/o | antrum |
| append, appendic | append/o, appendic/o | appendix |
| bil, chol | bil/i, chol/e, chol/o | bile, gall |
| bucc | bucc/o | cheek |
| cec | cec/o | cecum |
| cholangi/o | cholangi/o | bile duct |
| cholecyst | cholecyst/o | gallbladder |
| choledoch | choledoch/o | common bile duct |
| col, colon | col/o, colon/o | colon |
| dent, dent, odont | dent/o, dent/i, odont/o | tooth or teeth |
| diverticul | diverticul/o | diverticulum |
| duoden | duoden/o | duodenum |
| enter | enter/o | intestine |
| esophag | esophag/o | esophagus |
| gastr | gastr/o | stomach |
| gingiv | gingiv/o | gum |
| gnath | gnath/o | jaw |
| hepat | hepat/o | liver |
| herni | herni/o | hernia |
| ile | ile/o | ileum |
| jejun | jejun/o | jejunum |
| labi, cheil | labi/o, cheil/o | lip |
| lingu, gloss | lingu/o, gloss/o | tongue |
| or, stoma, stomat | or/o, stoma, stomat/o | mouth |
| palat | palat/o | palate |
| pancreat | pancreat/o | pancreas |
| peritone | peritone/o | peritoneum |
| pylor | pylor/o | pylorus or pyloric sphincter |
| rect, proct | rect/o, proct/o | rectum |
| sial | sial/o | saliva, salivary gland or salivary duct |
| sigmoid | sigmoid/o | sigmoid colon |
| steat | steat/o | fat |
| uvul | uvul/o | uvula |
Here are the more detailed review flashcards for this topic.
💡 Practice Quiz
- Common Word Roots for Digestive System (Part 1) [Practice Quiz]
- Common Word Roots for Digestive System (Part 2) [Practice Quiz]
- Common Word Roots for Digestive System (Part 3) [Practice Quiz]
- Common Word Roots for Digestive System (Part 4) [Practice Quiz]
Common Word Roots for Urinary System
| Word Root | Combining Form | Body Part or Condition |
|---|---|---|
| albumin | albumin/o | albumin |
| azot | azot/o | urea; nitrogen |
| calic, cali | calic/o, cali/o | calyx |
| cyst, vesic | cyst/o, vesic/o | urinary bladder |
| glomerul | glomerul/o | glomerulus |
| hydr | hydr/o | water |
| lith | lith/o | stone or calculus |
| meat | meat/o | meatus |
| pyel | pyel/o | renal pelvis |
| ren, nephr | ren/o, nephr/o | kidney |
| ur, urin | ur/o, urin/o | urine or urinary tract |
| ureter | ureter/o | ureter |
| urethr | urethr/o | urethra |
Here are the more detailed review flashcards for this topic.
💡 Practice Quiz
Common Word Roots for Male Reproductive System
| Word Root | Combining Form | Body Part or Condition |
|---|---|---|
| andr | andr/o | male |
| balan | balan/o | glans penis |
| epididym | epididym/o | epididymis |
| gonad | gonad/o | gonad |
| osche, scrot | osche/o, scrot/o | scrotum |
| pen, phall | pen/o, pen/i, phall/o | penis |
| preputi, posth | preputi/o, posth/o | prepuce (foreskin) |
| prostat | prostat/o | prostate gland |
| semin | semin/i | semen |
| sperm, spermat | sperm/o, spermat/o | spermatozoon (sperm) |
| test, testicular, orch, orchi, orchid | test/o, testicular/o, orch/o, orchi/o, orchid/o | testis (testicle) |
| urethr | urethr/o | urethra |
| vas | vas/o | vas deferens (also refers to vessel) |
| vesicul | vesicul/o | seminal vesicle |
Here are the more detailed review flashcards for this topic.
💡 Practice Quiz
Common Word Roots for Female Reproductive System
| Word Root | Combining Form | Body Part or Condition |
|---|---|---|
| amni | amni/o | amnion (amniotic sac) |
| cervic, trachel | cervic /o, trachel/o | cervix (also refers to neck) |
| clitor, clitorid | clitor/o, clitorid/o | clitoris |
| embry | embry/o | embryo |
| endometri | endometri/o | endometrium |
| fet | fet/o | fetus |
| gravid | gravid/o | pregnant woman |
| gyn, gynec | gyn/o, gynec/o | woman |
| hymen | hymen/o | hymen |
| lact, galact | lact/o, galact/o | milk |
| mamm, mast | mamm/o, mast/o | breast (mammary gland) |
| men | men/o | menstruation |
| nat | nat/i | birth |
| oo, ov | oo, ov/o, ov/i | ovum, egg cell |
| ovari, oophor | ovari/o, oophor/o | ovary |
| para | para | has given birth |
| pelv | pelv/i | pelvis, pelvic bones or pelvic cavity |
| perine | perine/o | perineum |
| salping | salping/o | uterine tube or fallopian tube |
| toc | toc/o | labor |
| uter, metr, hyster | uter/o, metr/o, metr/i, hyster/o | uterus |
| vagin, colp | vagin/o, colp/o | vagina |
| vulv, episi | vulv/o, episi/o | vulva |
Here are the more detailed review flashcards for this topic.
💡 Practice Quiz
- Common Word Roots for Female Reproductive System (Part 1) [Practice Quiz]
- Common Word Roots for Female Reproductive System (Part 2) [Practice Quiz]
Common Word Roots for Endocrine System
| Word Root | Combining Form | Body Part or Condition |
|---|---|---|
| aden | aden/o | gland |
| adren, adrenal | adren/o, adrenal/o | adrenal gland or epinephrine |
| adrenocortic | adrenocortic/o | adrenal cortex |
| calc | calc/i | calcium |
| endocrin | endocrin/o | endocrine glands or system |
| insul | insul/o | pancreatic islets |
| kal | kal/i | potassium |
| natr | natr/o | sodium |
| parathyr, parathyroid | parathyr/o, parathyroid/o | parathyroid gland |
| pituitar, hypophys | pituitar/o, hypophys/o | pituitary gland (hypophysis) |
| thyr, thyroid | thyr/o, thyroid/o | thyroid gland |
Here are the more detailed review flashcards for this topic.
💡 Practice Quiz
Common Word Roots for Nervous System
| Word Root | Combining Form | Body Part or Condition |
|---|---|---|
| cephal | cephal/o | head |
| cerebell | cerebell/o | cerebellum |
| cerebr | cerebr/o | cerebrum |
| cortic | cortic /o | cerebral cortex |
| dur | dur/o | dura mater |
| encephal | encephal/o | brain |
| esthesi | esthesi/o | sensation |
| gangli, ganglion | gangli/o, ganglion/o | ganglion |
| gli | gli/o | neuroglia |
| medull | medull/o | medulla oblongata |
| mening, meningi | mening/o, meningi/o | meninges |
| myel | myel/o | spinal cord |
| narc | narc /o | stupor; numbness |
| neur, neur | neur/o, neur/i | nervous system or nerve |
| phas | phas/o | speech |
| poli | poli/o | gray matter |
| psych, ment | psych/o, ment/o | mind |
| radic, radicul, rhiz | radic/o, radicul/o, rhiz/o | nerve root |
| somn, somn | somn/o, somn/i | sleep |
| thalam | thalam/o | thalamus |
Here are the more detailed review flashcards for this topic.
💡 Practice Quiz
- Common Word Roots for Nervous System (Part 1) [Practice Quiz]
- Common Word Roots for Nervous System (Part 2) [Practice Quiz]
Common Word Roots for Sensory System
| Word Root | Combining Form | Body Part or Condition |
|---|---|---|
| acoust, acous | acoust/o, acous/o | sound or hearing |
| audi | audi/o | hearing |
| chori, choroid | chori/o, choroid/o | choroid |
| cochle | cochle/o | cochlea |
| conjunctiv | conjunctiv/o | conjunctiva |
| corne, kerat | corne/o, kerat/o | cornea or horn |
| cycl | cycl/o | ciliary body or ciliary muscle |
| dacryocyst | dacryocyst/o | lacrimal sac |
| ir, irit, irid | ir/o, irit/o, irid/o | iris |
| labyrinth | labyrinth/o | labyrinth (inner ear) |
| lacrim, dacry | lacrim/o, dacry/o | tear or tear duct |
| lent, phak, phac | lent/i, phak/o, phac/o | lens |
| mastoid | mastoid/o | mastoid bone |
| myring, tympan | myring/o, tympan/o | tympanic membrane (eardrum) |
| opt, ocul, ophthalm | opt/o, ocul/o, ophthalm/o | eye |
| ot, aur, aur | ot/o, aur/o, aur/i | ear |
| palpebr, blephar | palpebr/o, blephar/o | eyelid |
| phot | phot/o | light |
| pupill, core, cor | pupill/o, core/o, cor/o | pupil |
| retin | retin/o | retina |
| salping | salping/o | auditory eustachian tube (also refers to the fallopian tube of the uterus) |
| scler | scler/o | sclera |
| staped, stapedi | staped/o, stapedi/o | stapes (middle ear bone) |
| uve | uve/o | uvea |
| vestibul | vestibul/o | vestibule of the inner ear |
Here are the more detailed review flashcards for this topic.
💡 Practice Quiz
- Common Word Roots for Sensory System (Part 1) [Practice Quiz]
- Common Word Roots for Sensory System (Part 2) [Practice Quiz]
Common Word Roots for Skeletal System
| Word Root | Combining Form | Body Part or Condition |
|---|---|---|
| ankyl | ankyl/o | stiff, bent |
| aponeur | aponeur/o | aponeurosis |
| arthr | arthr/o | joint |
| burs | burs/o | bursa |
| carp | carp/o | carpals, wrist |
| chondr | chondr/o | cartilage |
| clavic, clavicul | clavic/o, clavicul/o | clavicle (collarbone) |
| coccy, coccyg | coccy, coccyg/o | coccyx |
| cost | cost/o | rib |
| crani | crani/o | skull or cranium |
| disk | disk/o | intervertebral disk |
| femor | femor/o | femur (upper leg bone) |
| fibul | fibul/o | fibula (outer lower leg bone) |
| humer | humer/o | humerus (upper arm bone) |
| ili | ili/o | ilium |
| ischi | ischi/o | ischium |
| kinesi | kinesi/o | movement (motion) |
| kyph | kyph/o | humpback |
| lord | lord/o | curve; swayback |
| lumb | lumb/o | loin (lumbar region of the spine) |
| mandibul | mandibul/o | mandible (lower jawbone) |
| maxill | maxill/o | maxilla (upper jawbone) |
| menisc | menisc/o | meniscus |
| myel | myel/o | bone marrow (also refers to the spinal cord) |
| myel | myel/o | spinal cord (also refers to the bone marrow) |
| oste | oste/o | bone |
| patell | patell/o | patella (kneecap) |
| pelv, pelv | pelv/i, pelv/o | pelvis (pelvic bone) |
| phalang | phalang/o | phalanges (finger and toes bones) |
| pub | pub/o | pubis |
| rachi | rachi/o | vertebrae (spinal column) |
| radi | radi/o | radius (lateral forearm bone) |
| sacr | sacr/o | sacrum |
| scapul | scapul/o | scapula (shoulder blade) |
| scoli | scoli/o | curved |
| spondyl, vertebr | spondyl/o, vertebr/o | vertebra |
| stern | stern/o | sternum (breastbone) |
| synov | synov/i | synovial fluid, joint, or membrane |
| tars | tars/o | tarsals (ankle bones) |
| ten, tendin, tend | ten/o, tendin/o, tend/o | tendon |
| tibi | tibi/o | tibia (inner lower leg bone) |
| uln | uln/o | ulna (medial forearm bone) |
Here are the more detailed review flashcards for this topic.
💡 Practice Quiz
- Common Word Roots for Skeletal System (Part 1) [Practice Quiz]
- Common Word Roots for Skeletal System (Part 2) [Practice Quiz]
- Common Word Roots for Skeletal System (Part 3) [Practice Quiz]
- Common Word Roots for Skeletal System (Part 4) [Practice Quiz]
Common Word Roots for Muscular System
| Word Root | Combining Form | Body Part or Condition |
|---|---|---|
| fasci | fasci/o | fascia |
| flex | flex/o | bend |
| in | in/o, fibr/o | fiber |
| kin, kinesi, kinet | kin/e, kinesi/o, kinet/o | movement |
| leiomy | leiomy/o | smooth visceral muscle |
| my, myos, muscul | my/o, myos/o, muscul/o | muscle |
| myocardi | myocardi/o | cardiac muscle |
| rhabdomy | rhabdomy/o | skeletal or striated muscle |
| sarc | sarc/o | connective tissue; soft or flesh |
| ten, tendin | ten/o, tendin/o, tend/o | tendon |
| tens | tens/o | stretch; strain |
| ton | ton/o | tone |
Here are the more detailed review flashcards for this topic.
💡 Practice Quiz
Common Word Roots for Integumentary System
| Word Root | Combining Form | Body Part or Condition |
|---|---|---|
| derm, dermat, cutane | derm/o, dermat/o, cutane/o | skin |
| hidr, idr | hidr/o, idr/o | sweat |
| hirsut | hirsut/o | hairy, rough |
| melan | melan/o | melanin or dark |
| myc | myc/o | fungus |
| necr | necr/o | death |
| onych, ungu | onych/o, ungu/o | nail |
| pachy | pachy/o | thick |
| rhytid | rhytid/o | wrinkles |
| seb | seb/o | sebum or sebaceous gland |
| staphyl | staphyl/o | grapelike clusters (also refers to uvula) |
| strept | strept/o | twisted chains or strips |
| trich | trich/o | hair |
| xer | xer/o | dry |
Here are the more detailed review flashcards for this topic.
💡 Practice Quiz
Prefixes
The prefix is a word part added to the beginning of a medical term that alters the meaning of the word root. A prefix can describe the quantity, quality, location, color, direction, time, degree, or status of a word root. Medical terms do not all have prefixes.
*When written alone or detached from other medical word parts, the prefix is sometimes followed by a hyphen (-). For example, in the medical term hypertension, (hyper-) is written with a hyphen to distinguish it as a prefix.
Common Prefixes
A list of commonly used prefixes is provided below, categorized accordingly.
Prefixes that Describe the Quantity or Number
| Prefix | Number |
|---|---|
| nulli- | none |
| semi-, hemi- | half or partial |
| poly-, multi- | many |
| prim(i)- | first |
| mon(o)-, uni-, hapl(o)- | one, single |
| di-, dipl(o)-, bi- | two, double |
| tri- | three |
| quadr(i)-, tetr(a)- | four |
| pent(a)- | five |
| hex(a)- | six |
| hept(a)- | seven |
| oct(o)-, oct(a)- | eight |
| nona-,noni- | nine |
| deci-, deca- | ten |
| cent(i)- | hundred |
| milli- | thousand |
Here are the more detailed review flashcards for this topic.
💡 Practice Quiz
Prefixes that Describe the Color
| Prefix | Color |
|---|---|
| chlor(o)- | green |
| cirrh(o)-, jaund(o)-, xanth(o)- | yellow |
| cyan(o)- | blue |
| erythr(o)-, rubr(o)-, rhod(o)-, eosin(o)- | red |
| glauc(o)-, poli(o)- | grey or silver |
| leuk(o)-, alb-, albin(o)- | white |
| melan(o)- | black |
| purpur-, porphyr- | purple |
Here are the more detailed review flashcards for this topic.
💡 Practice Quiz
Prefixes that Describe the Size
| Prefix | Size |
|---|---|
| micr(o)- | small |
| macr(o)-, mega(lo)- | large |
| iso-, equi- | equal |
Here are the more detailed review flashcards for this topic.
💡 Practice Quiz
Prefixes that Describe the Degree
| Prefix | Degree |
|---|---|
| hyp(o)-, sub- | low, below normal |
| hyper-, super-, ultra- | high, above normal |
| norm(o)- | normal |
Here are the more detailed review flashcards for this topic.
💡 Practice Quiz
Prefixes that Describe the Position or Direction
| Prefix | Position or Direction |
|---|---|
| ab- | away |
| ad- | toward |
| ambi- | both |
| ante-, anter(o)-, ventr(i)-, ventr(o)- | anterior (front) |
| dextr(o)- | right |
| ect(o)-, ex(o)-, extra-, extro- | out, outside |
| end(o)-, intra-, intro- | inside |
| ep(i)-, supra-, super- | above |
| inter- | between |
| later(o)- | lateral or side |
| mes(o)-, medi(o)-,medi(a)- | middle |
| juxta- | near |
| para- | near, apart from, abnormal |
| peri- , circum- | around |
| poster(o)-, dors(i)-, dors(o)- | posterior (back) |
| sinistr(o)-, levo- | left |
| sub-, infra- | below |
| tele-, telo- | distant |
| trans-, dia-, per- | through |
Here are the more detailed review flashcards for this topic.
💡 Practice Quiz
Prefixes that Describe the Time or Speed
| Prefix | Time or Speed |
|---|---|
| ante-, pre-, pro- | before |
| brady- | slow |
| chron(o)- | time |
| neo- | new, recent |
| post- | after |
| re- | again |
| retr(o)- | back, backward |
| tachy- | fast |
Here are the more detailed review flashcards for this topic.
💡 Practice Quiz
Prefixes that Describe the Status
| Prefix | Status |
|---|---|
| a-, an-, non-,un- | not, without |
| anti-, contra- | against |
| de- | away from, without |
| dis- | apart, separate |
| eu- | normal |
| heter(o)- | other, different |
| hom(o)- | same, similar |
| mal- | bad |
| dys- | bad, difficult, painful, abnormal |
| orth(o)- | straight; correct |
| poikilo- | irregular, varied |
| pseud(o)- | false |
Here are the more detailed review flashcards for this topic.
💡 Practice Quiz
Suffix
The use of suffixes changes the meaning of medical terminology. It is added to the end of a medical word to typically describe procedures, conditions, functions or just to make a medical word a noun or an adjective.
For example in the word arthritis which means inflammation of the joints, the word root “arthr” means joints while the suffix “-itis” means inflammation. Like the prefix, the suffix when detached in a medical term is written with a hyphen (-) before the word part as demonstrated for the suffix “-itis“.
In other cases, the suffixes have no real meaning to them and their sole purpose is to make or form the medical term into a noun or an adjective. A good example is the suffix -um of the word endocardium. The prefix endo- means inside, the root cardi means heart, and the suffix -um makes this medical term turn into a noun.
Common Suffixes
The following are examples of suffixes that are categorized accordingly.
Suffixes that Describe the State or Form
| Suffixes that Forms Noun | Meaning |
|---|---|
| -a, -e, -um, -is | noun ending with no specific meaning |
| -gen, genic | causing |
| -ia, -ism, iasis, -sis, -y | condition |
| -ian,- iatrics, -iatry, -ics,- ist, -logy | specialty |
| Suffixes that Forms Adjective | Meaning |
|---|---|
| -ac,-al, -ar(y), -form, -ic(al), -ile, -ior, -ory,-ous, -tic | pertaining to |
| -form, -oid | resembling |
Suffixes that Describe Surgery, Diagnosis & Procedure
| Suffix | Meaning |
|---|---|
| -(a)pheresis | removal |
| -centesis | surgical puncture |
| -desis | fusion of two parts into one |
| -ectomy | surgical removal |
| -gram | the record |
| -graph | instrument used to record |
| -graphy | process of recording |
| -metry, -meter | measurement |
| -opsy | looking at |
| -ostomy, -stomy | surgically creating a hole |
| -otomy, -tomy | surgical incision |
| -tome | surgical incision instrument or section; segment |
| -pexy | fix or secure |
| -plasty | surgical repair or reconstruction |
| -rrhaphy | surgical suturing |
| -scope | instrument used for viewing or examination |
| -scopic | pertaining to visual examination |
| -scopy | process of viewing with a scope |
| -tripsy | crushing or breaking up |
Here are the more detailed review flashcards for this topic.
💡 Practice Quiz
- Suffixes that Describe Surgery, Diagnosis & Procedure (Part 1) [Practice Quiz]
- Suffixes that Describe Surgery, Diagnosis & Procedure (Part 2) [Practice Quiz]
Suffixes that Describe Disease or Function
| Suffix | Disease or Function |
|---|---|
| -algia, -algesia, -dynia | pain |
| -asthenia | weakness |
| -carcinoma | cancerous tumor |
| -cardia | heart condition |
| -cele | hernia, swelling |
| -clasis, -clasia | breaking |
| -cyesis | pregnancy |
| -drome | running |
| -ectasia, -ectasis, -dilation, -dilatation | dilation |
| -edema | swelling |
| -emesis | vomiting |
| -emia | blood or blood condition |
| -itis | inflammation |
| -lysis | separating, dissolution |
| -malacia | softening |
| -megaly | enlargement |
| -necrosis | death of tissue |
| -oma | tumor |
| -opia | vision |
| -osis | abnormal condition |
| -paresis | slight paralysis |
| -pathy | disease |
| -penia | abnormal reduction in number |
| -pepsia | digestion |
| -phagia | swallowing, eating |
| -phasia | speech |
| -pheresis | removal |
| -phil(ia) | affinity for, attraction |
| -phobia | irrational fear |
| -phoresis | transmit |
| -physis | growth |
| -plasia | formation, growth |
| -plasm | living substance, tissue |
| -plegia | paralysis |
| -pnea | breathing |
| -poiesis | formation |
| -ptosis | prolapse, drooping |
| -rrhage, -rrhagia | excessive bleeding |
| -rrhea | flow, discharge |
| -rrhexis | rupture |
| -salpinx | fallopian tube, uterine tube |
| -sarcoma | malignant tumor |
| -schisis | fissure, splitting |
| -sclerosis | hardening |
| -spasm | sudden, involuntary contraction of muscle |
| -stalsis | contraction |
| -stasis | control, stop |
| -stenosis | tightening |
| -thorax | chest, chest cavity |
| -tocia | labor, birth |
| -trophy | nourishment; development |
| -uria | urine, urination |
Here are the more detailed review flashcards for this topic.
💡 Practice Quiz
- Suffixes that Describe Disease or Function (Part 1) [Practice Quiz]
- Suffixes that Describe Disease or Function (Part 2) [Practice Quiz]
- Suffixes that Describe Disease or Function (Part 3) [Practice Quiz]
- Suffixes that Describe Disease or Function (Part 4) [Practice Quiz]
Plural Forms
Medical terms can have different rules regarding forming plural terms than the standard English terms, where we use es and s in the ending of the word. Following are the rules that are used in transforming singular medical terms to plurals:
Rule 1: For singular ending a, just add e to make it plural.
| Singular Form | Plural Form |
|---|---|
| areola | areolae |
| macula | maculae |
| retina | retinae |
| trachea | tracheae |
| vertebra | vertebrae |
Rule 2: For singular ending with ax , change the ax to aces.
| Singular Form | Plural Form |
|---|---|
| anthrax | anthraces |
| pneumothorax | pneumothoraces |
| thorax | thoraces |
Rule 3: For singular ending with ex or ix, change the ex or ix to ices.
| Singular Form | Plural Form |
|---|---|
| cortex | cortices |
| subcortex | subcortices |
| appendix | appendices |
| cervix | cervices |
| helix | helices |
Rule 4: For singular ending with is, change the is to es.
| Singular Form | Plural Form |
|---|---|
| cholelithiasis | cholelithiases |
| diabetis | diabetes |
| diagnosis | diagnoses |
| emesis | emeses |
| osteoporosis | osteoporoses |
Rule 5: For singular ending ma, just add ta to make it plural.
| Singular Form | Plural Form |
|---|---|
| blastoma | blastomata |
| edema | edemata |
| fibroma | fibromata |
| sarcoma | sarcomata |
| stigma | stigmata |
| stoma | stomata |
Rule 6: For singular ending nx (anx, inx, ynx), change nx to nges.
| Singular Form | Plural Form |
|---|---|
| larynx | larynges |
| meninx | meninges |
| phalanx | phalanges |
| pharynx | pharynges |
| salpinx | salpinges |
Rule 7: For singular ending on, change on to a.
| Singular Form | Plural Form |
|---|---|
| ganglion | ganglia |
| myelencephalon | myelencephala |
| spermatozoon | spermatozoa |
Rule 8: For singular ending um, change um to a.
| Singular Form | Plural Form |
|---|---|
| atrium | atria |
| bacterium | bacteria |
| clostridium | clostridia |
| diverticulum | diverticula |
| duodenum | duodena |
| endocardium | endocardia |
| endometrium | endometria |
| ostium | ostia |
| ovum | ova |
| reticulum | reticula |
Rule 9: For singular ending us, change us to i.
| Singular Form | Plural Form |
|---|---|
| bacillus | bacilli |
| calculus | calculi |
| canthus | canthi |
| embolus | emboli |
| malleus | mallei |
| meniscus | menisci |
| nucleus | nuclei |
| phallus | phalli |
| pylorus | pylori |
| radius | radii |
| thrombus | thrombi |
Rule 10: For singular ending y, change y to ies.
| Singular Form | Plural Form |
|---|---|
| arthroscopy | arthroscopies |
| biosy | biopsies |
| cavity | cavities |
| epilepsy | epilepsies |
| laryngoscopy | laryngoscopies |
| microscopy | microscopies |
| narcolepsy | narcolepsies |
| retinoscopy | retinoscopies |
| therapy | therapies |
Exemptions
Even though there are these rules for medical terms, you will notice in dictionaries that the standard English rules like using -s and -es are also being used as acceptable plural forms in several medical terms. For example, the word retina is pluralized as retinae when following the rules above, but the word retinas is also acceptable.
A second example is the word virus, where “viruses” is the correct plural form instead of “viri” not adhering to the rules above which states that singular form ending with the letter -us should be changed to -i.