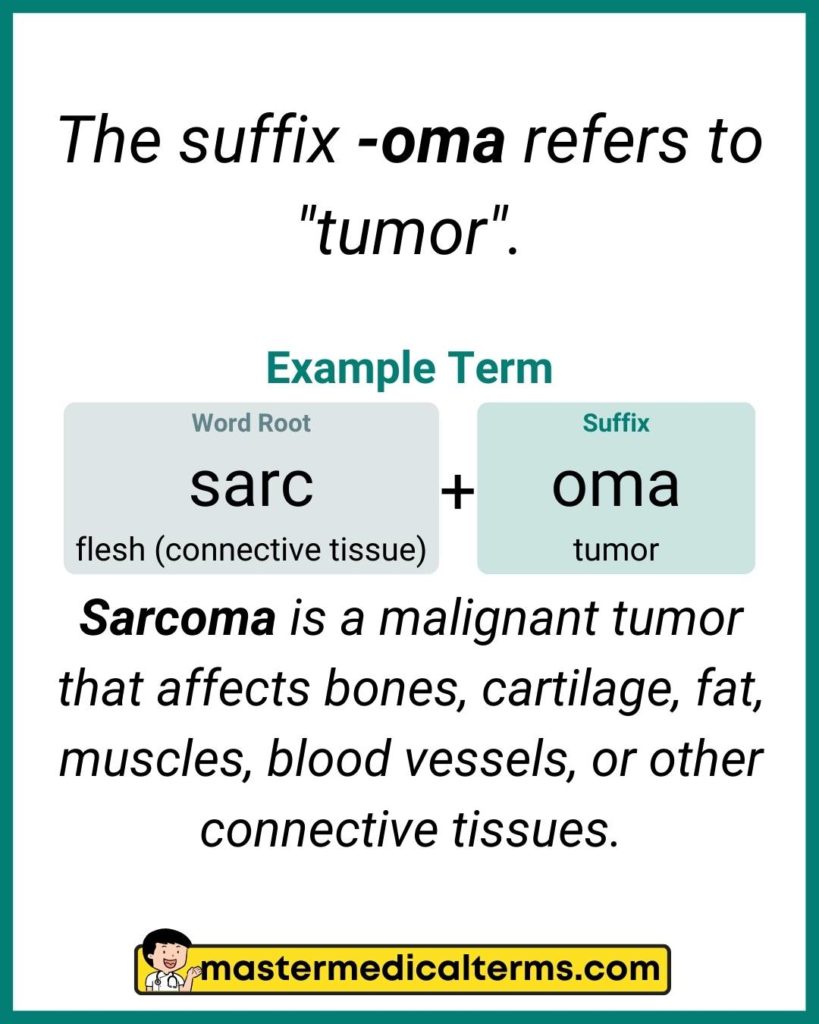
The medical suffix term -oma refers to “tumor”.
Example Word: sarc/oma
Word Breakdown: Sarc is a word root that pertains to “flesh (connective tissue)”, and -oma refers to “tumor”.
Definition: Sarcoma is a malignant tumor that affects bones, cartilage, fat, muscles, blood vessels, or other connective tissues.
More Examples of Medical Terms Ending in -oma
Adenoma: aden ( “gland”) + –oma ( “tumor”)
Definition: A benign tumor that originates in glandular tissue.
Atheroma: ather ( “fatty substance”) + –oma ( “tumor”)
Definition: A fatty tumor or lesion that typically forms in the inner lining of arterial walls.
Carcinoma: carcin ( “cancer”) + –oma ( “tumor”)
Definition: A type of cancer that originates in epithelial cells, which line the surface of organs and tissues.
Chondroma: chondr ( “cartilage”) + -oma ( “tumor”)
Definition: A benign tumor that arises from cartilage cells.
Cystadenoma: cyst ( “bladder”) + aden ( “gland”) + –oma ( “tumor”)
Definition: A type of benign tumor that originates in glandular tissue and forms within a cyst.
Fibroma: fibr ( “fibrous tissue”) + –oma ( “tumor”)
Definition: A benign tumor that arises from fibrous tissue.
Glioma: gli ( “glial cells of the brain”) + –oma ( “tumor”)
Definition: A type of brain tumor that originates in glial cells.
Lipoma: lip ( “fat”) + –oma ( “tumor”)
Definition: A benign tumor made up of fat cells.
Lymphoma: lymph ( “lymphatic system”) + –oma ( “tumor”)
Definition: A type of cancer that originates in lymphatic tissue.
Meningioma: meningi ( “meninges, the protective membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord“) + –oma ( “tumor”)
Definition: A type of brain tumor that originates in the meninges.
Myoma: my ( “muscle”) + –oma ( “tumor”)
Definition: A benign tumor that originates in muscle tissue.
Osteoma: oste ( “bone”) + –oma ( “tumor”)
Definition: A benign tumor that originates in bone tissue.
Papilloma: papill ( “nipple-like projection”) + –oma ( “tumor”)
Definition: A benign tumor that is made up of cells that project outward from a central axis.