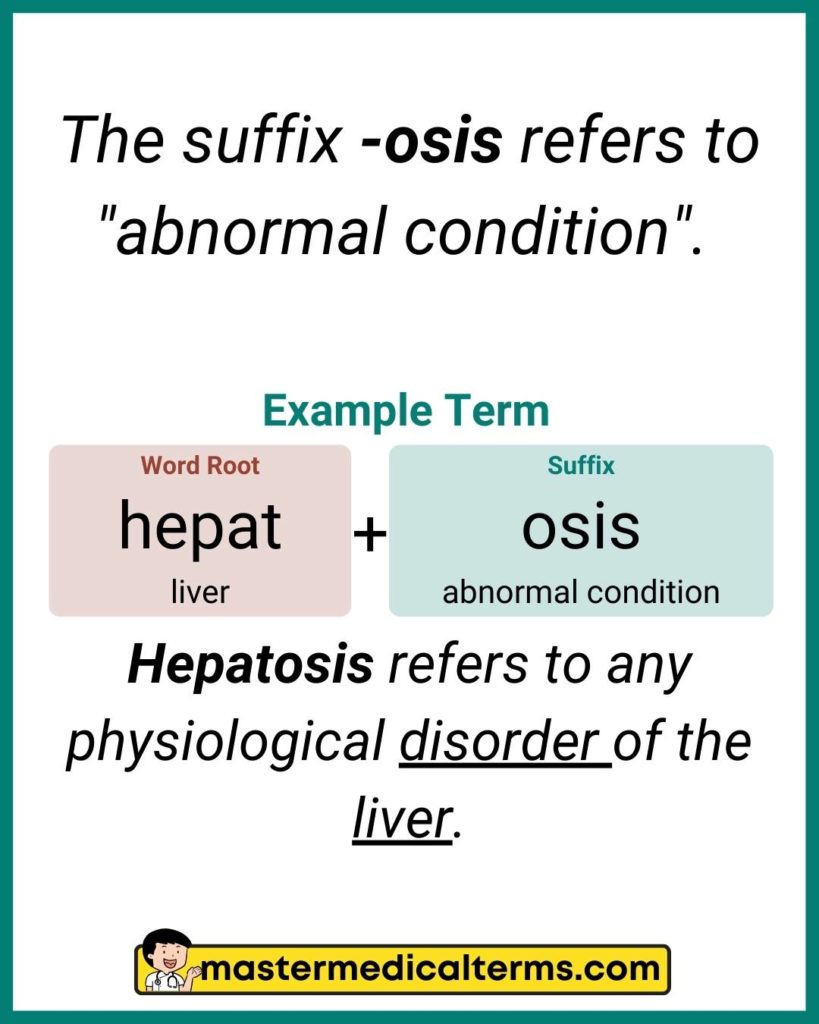
The medical suffix term -osis refers to “abnormal condition”.
Example Word: hepat/osis
Word Breakdown: Hepat is a word root that means “liver”, and -osis refers to “abnormal condition”.
Definition: Hepatosis refers to any physiological disorder of the liver.
Examples of Medical Terms Ending in -osis
Acidosis: acid ( “acid”) + –osis ( “abnormal condition”)
Definition: A condition in which the body’s pH level becomes too acidic, typically caused by an accumulation of acid or a decrease in base.
Alkalosis: alkal/o ( “alkali”) + –osis ( “abnormal condition”)
Definition: A condition in which the body’s pH level becomes too alkaline, typically caused by a loss of acid or an increase in base, symptoms are lightheadedness, muscle twitching and tingling.
Atherosclerosis: ather/o ( “fatty deposits”) + scler ( “hardening”) + –osis ( “abnormal condition”)
Definition: A condition in which fatty deposits build up in the walls of the arteries, leading to hardening and narrowing of the vessels.
Arteriosclerosis: arteri/o ( “artery”) + scler ( “hardening”) + –osis ( “abnormal condition”)
Definition: A condition in which the arteries become hard and narrowed due to the buildup of plaque.
Cirrhosis: cirrh/o ( “yellowing”) + –osis ( “abnormal condition”)
Definition: A condition in which the liver is damaged, leading to scarring and poor function.
Nephrosis: nephr ( “kidney”) + –osis ( “abnormal condition”)
Definition: A condition that affects the kidneys, characterized by the loss of protein in the urine and swelling in the body.
Osteoporosis: oste/o ( “bone”) + por ( “pore” or “spongy”) + –osis ( “abnormal condition”)
Definition: A condition characterized by a loss of bone density, making bones brittle and more prone to fractures.
Thrombosis: thromb/o ( “blood clots”) + –osis ( “abnormal condition”)
Definition: The formation of a blood clot within a blood vessel, which can restrict or block blood flow.
Necrosis: necr ( “death”) + –osis ( “condition”)
Definition: A condition characterized by the death of cells or tissue, typically caused by injury or disease.