By reviewing this flashcard review list, you will be able to identify and expand your knowledge of digestive system combining forms and root words. Check out the quiz version of this flashcard if you want to see how much you remember.
#1 abdomin/o , celi/o, lapar/o
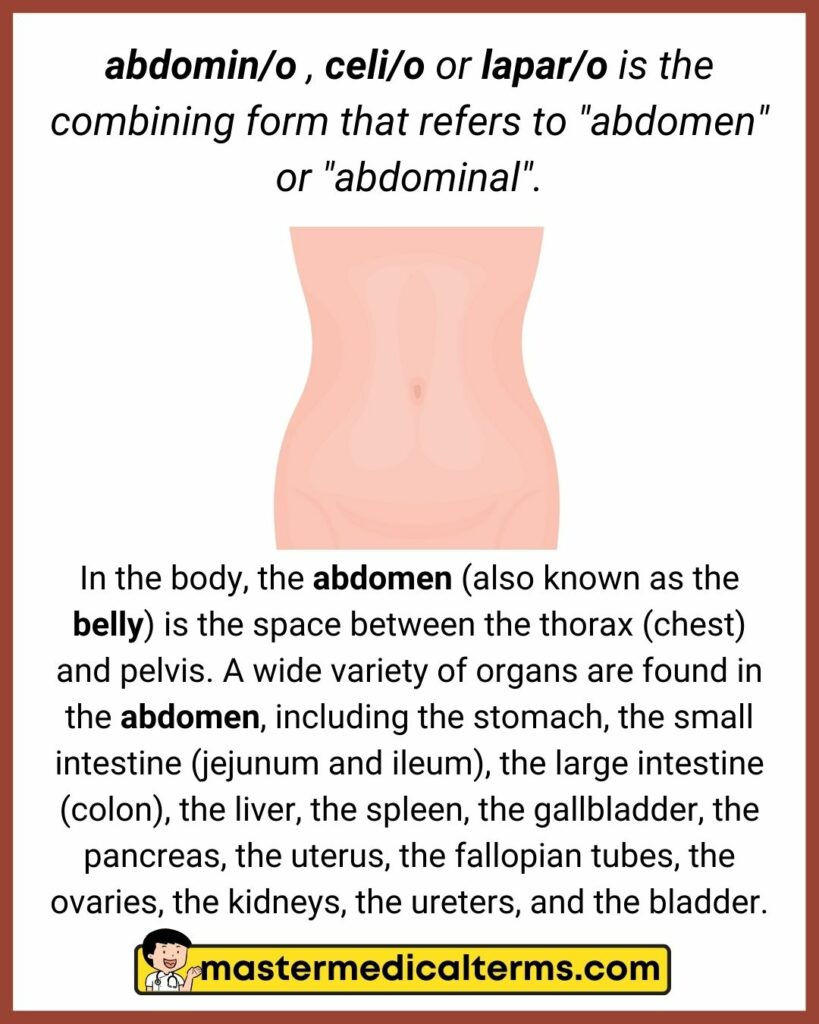
abdomin/o , celi/o or lapar/o is the combining form that refers to "abdomen" or "abdominal".
In the body, the abdomen (also known as the belly) is the space between the thorax (chest) and pelvis. A wide variety of organs are found in the abdomen, including the stomach, the small intestine (jejunum and ileum), the large intestine (colon), the liver, the spleen, the gallbladder, the pancreas, the uterus, the fallopian tubes, the ovaries, the kidneys, the ureters, and the bladder.
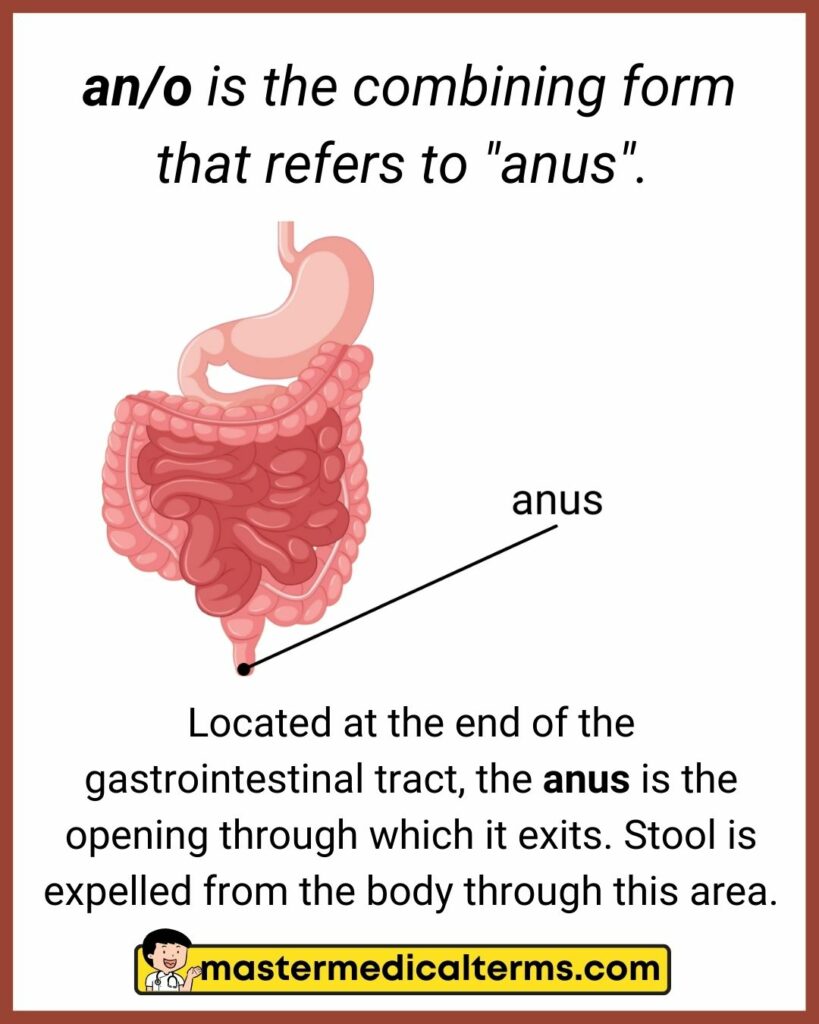
#2 an/o
#3 antr/o
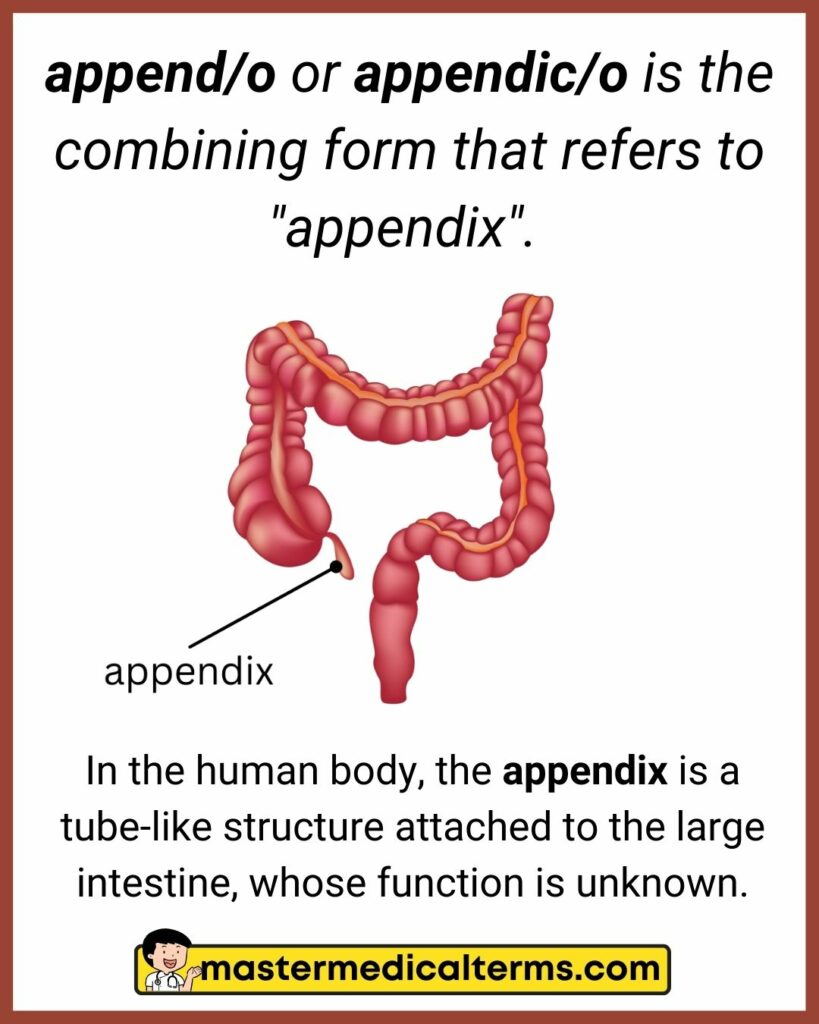
#4 append/o, appendic/o
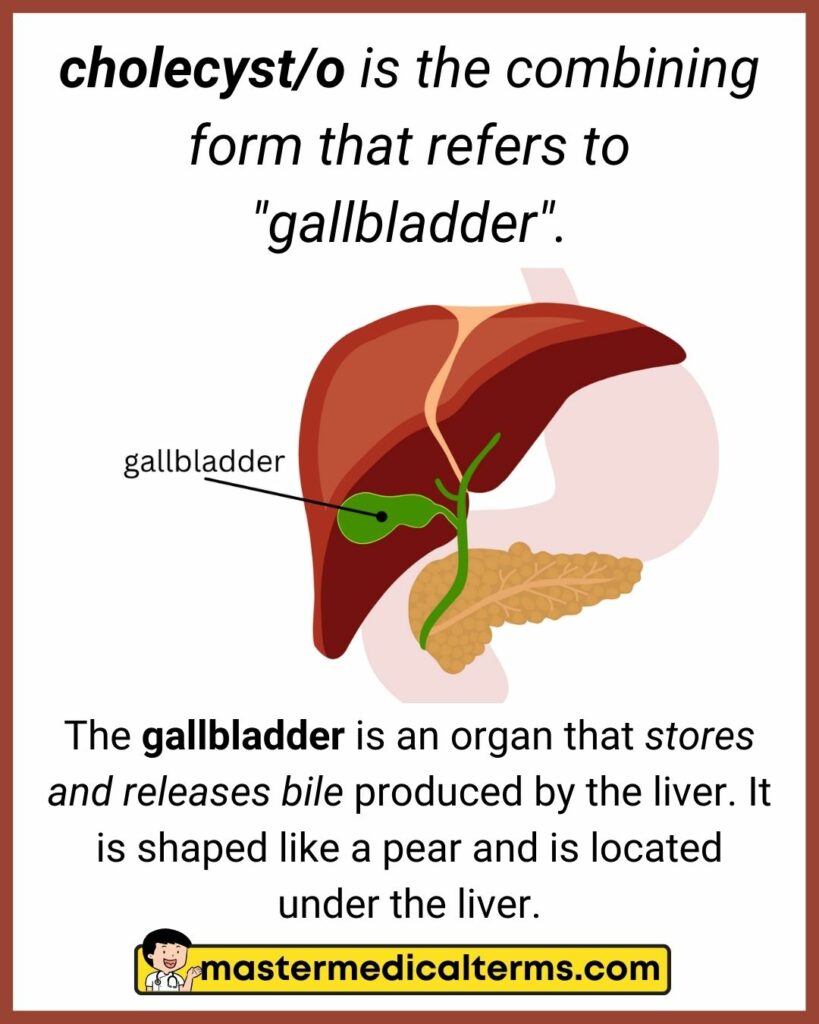
#5 bil/i, chol/e
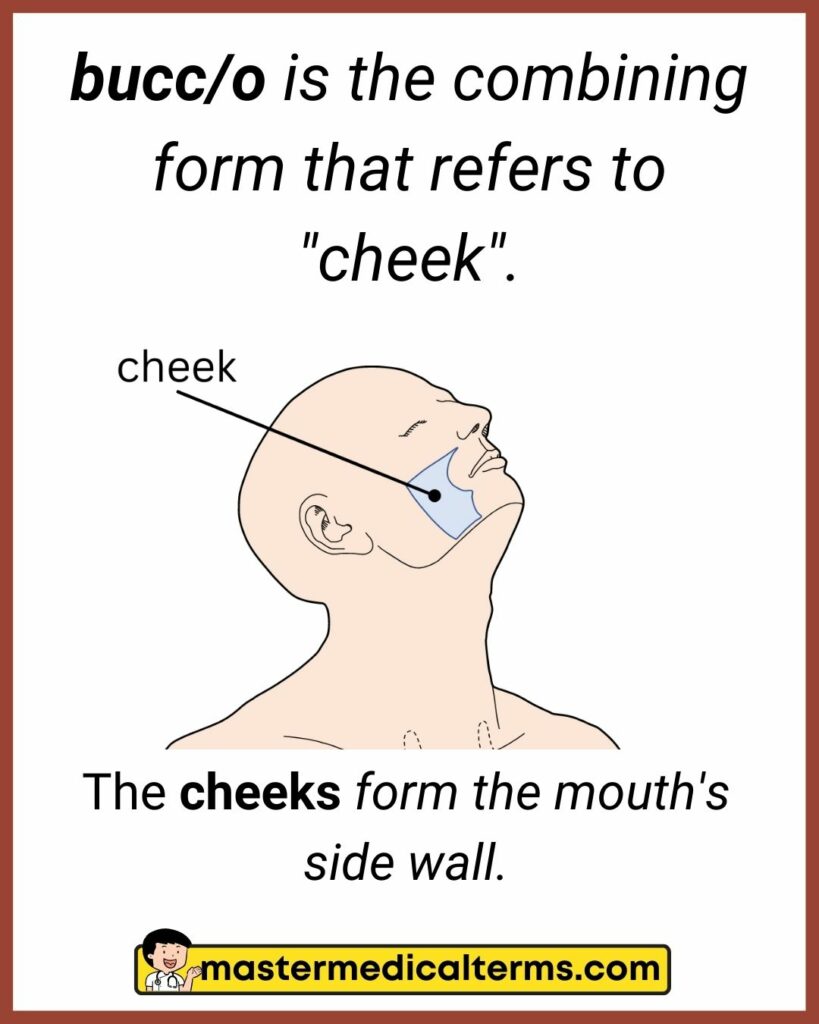
#6 bucc/o
#7 cec/o
#8 cholangi/o
#9 cholecyst/o
#10 choledoch/o
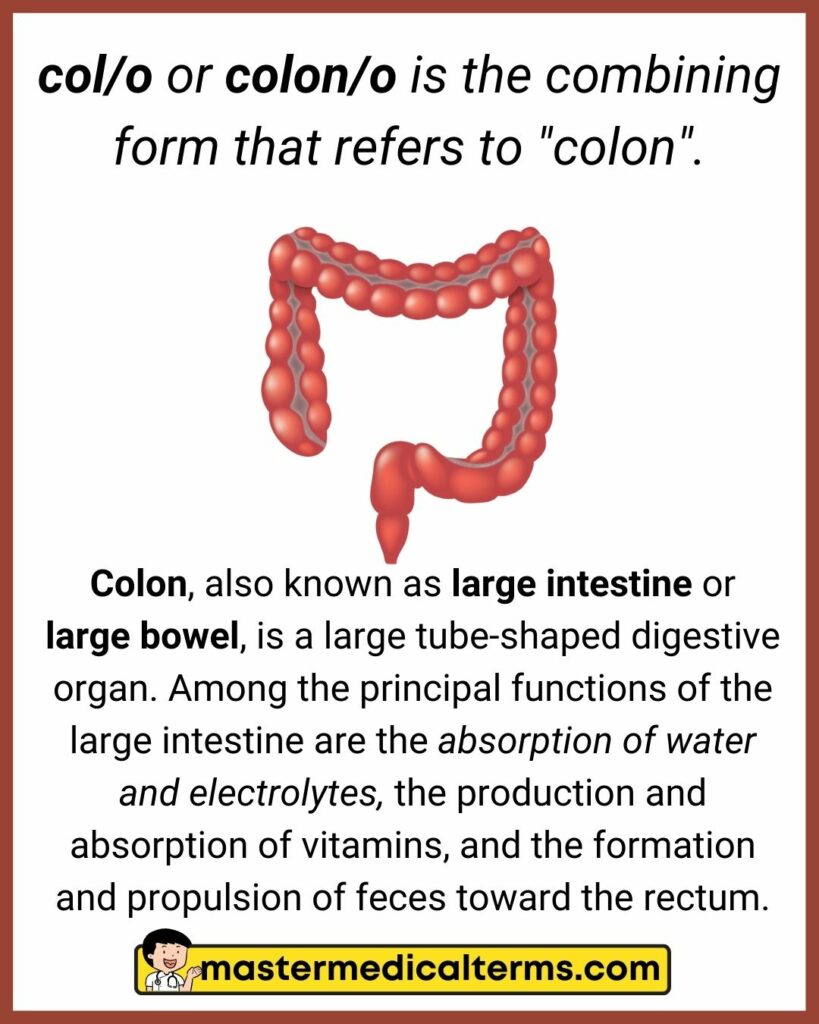
#11 col/o, colon/o
col/o or colon/o is the combining form that refers to "colon".
Colon, also known as large intestine or large bowel, is a large tube-shaped digestive organ. Among the principal functions of the large intestine are the absorption of water and electrolytes, the production and absorption of vitamins, and the formation and propulsion of feces toward the rectum.
#12 dent/o, dent/i, odont/o
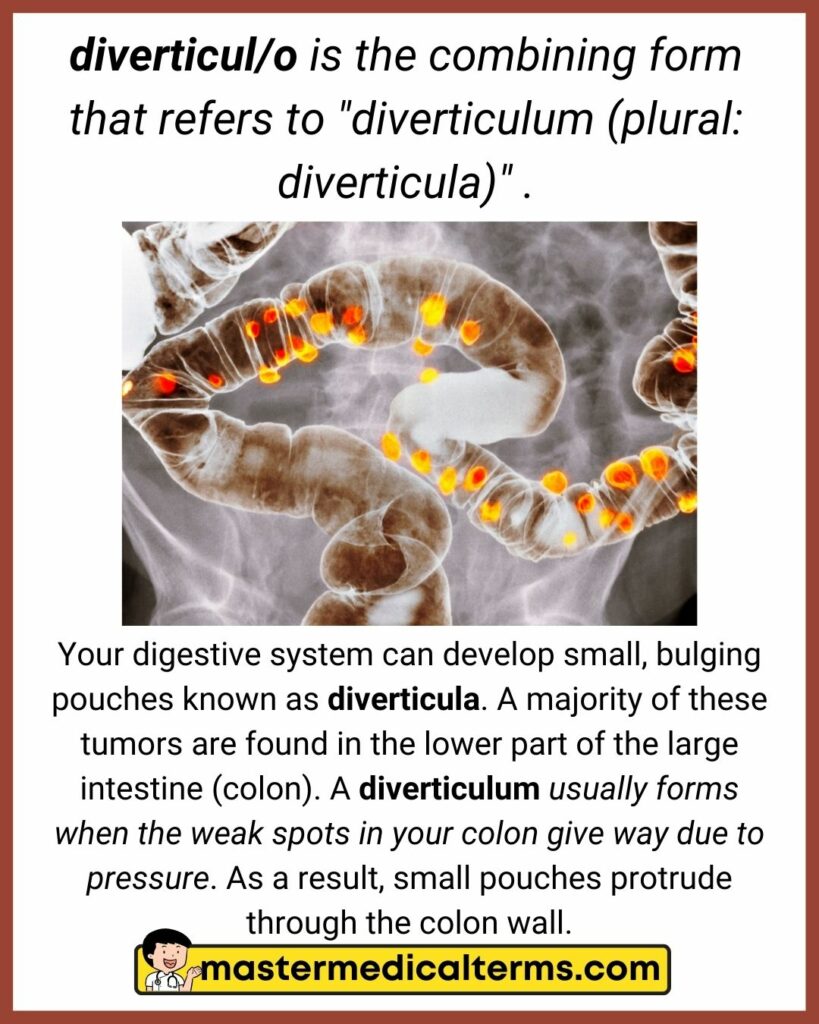
#13 diverticul/o
diverticul/o is the combining form that refers to "diverticulum (plural: diverticula)" .
Your digestive system can develop small, bulging pouches known as diverticula. A majority of these tumors are found in the lower part of the large intestine (colon). A diverticulum usually forms when the weak spots in your colon give way due to pressure. As a result, small pouches protrude through the colon wall.
#14 duoden/o
duoden/o is the combining form that refers to "duodenum".
Located in the small intestine near the stomach, the duodenum is the first part that connects to the stomach. Food from the stomach is also digested in the duodenum. The duodenum absorbs nutrients (such as vitamins, minerals, carbohydrates, fats, and proteins) from food.
#15 enter/o
#16 esophag/o
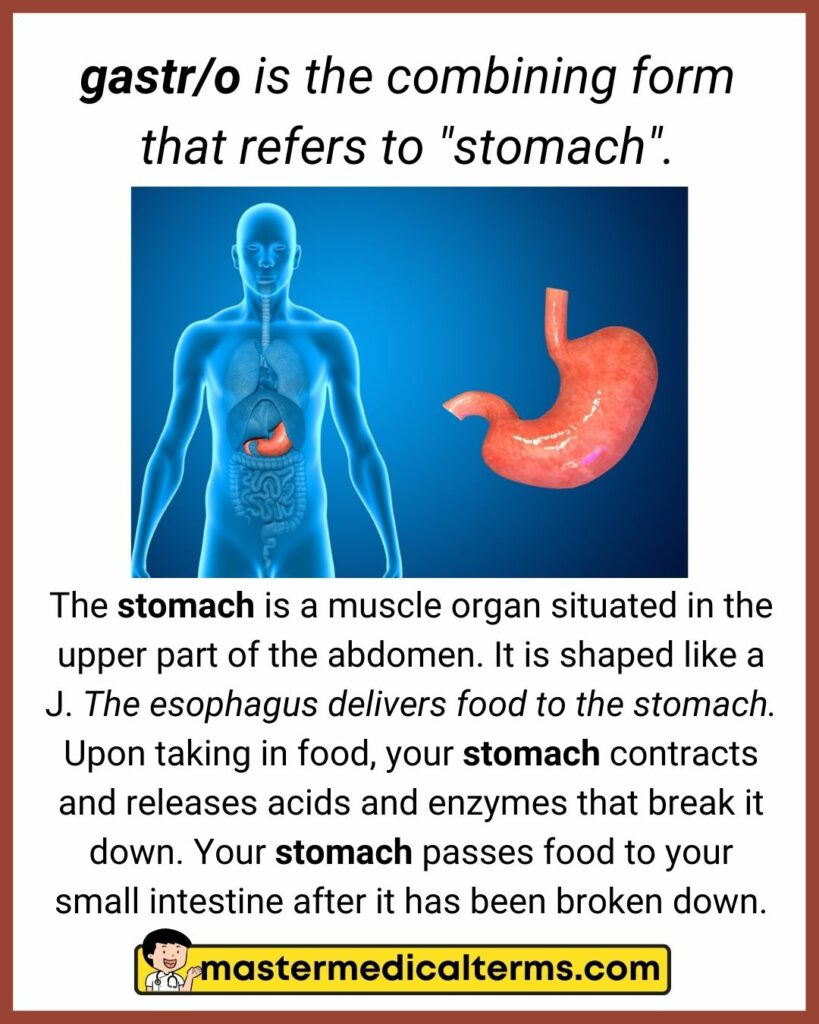
#17 gastr/o
gastr/o is the combining form that refers to "stomach".
The stomach is a muscle organ situated in the upper part of the abdomen. It is shaped like a J. The esophagus delivers food to the stomach. Upon taking in food, your stomach contracts and releases acids and enzymes that break it down. Your stomach passes food to your small intestine after it has been broken down.
Examples of Medical Terms Starting with Gastr/o
Gastrectomy: gastr ( "stomach") + -ectomy ( "removal")
Definition: Surgical removal of all or part of the stomach.
Gastric: gastr ( "stomach") + -ic ( "pertaining to")
Definition: Pertaining to the stomach.
Gastritis: gastr ( "stomach") + -itis ( "inflammation")
Definition: Inflammation of the stomach lining.
Gastroenteritis: gastr/o ( "stomach") + enter ( "intestine") + -itis ( "inflammation")
Definition: Inflammation of both the stomach and the intestines.
Gastroenterologist: gastr/o ( "stomach") + enter ( "intestine") + -ologist ( "one who studies")
Definition: Doctors who specialize in diagnosing and treating stomach and intestinal disorders.
Gastroesophageal: gastr/o ( "stomach") + esophag ( "related to the esophagus") + -eal ("pertaining to").
Definition: Pertaining to the stomach and esophagus.
Gastrointestinal: gastr/o ( "stomach") + intestin ( "related to the intestines") + -al ("pertaining to')
Definition: Pertaining to the stomach and intestines.
Gastrologist: gastr/o ( "stomach") + -ologist ( "one who studies")
Definition: A doctor who specializes in the diagnosis and treatment of disorders of the stomach.
Gastronomy: gastr/o ( "stomach") + -nomy ( "study of")
Definition: The study of the science of food and its relation to the body and culture.
Gastroparesis: gastr/o ( "stomach") + -paresis ( "partial paralysis")
Definition: A condition in which the muscles of the stomach are partially paralyzed, causing difficulty in digesting food.
Gastroplasty: gastr/o ( "stomach") + -plasty ( "surgical repair")
Definition: A surgical procedure to repair the stomach, typically used to treat conditions such as obesity or Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD).
Gastroscopy: gastr/o ( "stomach") + -scopy ( "examination")
Definition: An examination of the inside of the stomach using a lighted, flexible tube inserted through the mouth.
Gastrostomy: gastr/o ( "stomach") + -stomy ( "creation of an opening")
Definition: A surgical procedure to create an opening in the stomach, typically used to provide a way to feed a person who is unable to eat or drink through the mouth.
Gastrotomy: gastr/o ( "stomach") + -tomy ( "incision")
Definition: Surgical incision of the stomach, typically used to diagnose or treat conditions such as Gastric ulcers, Gastric cancer.
#18 gingiv/o
#19 gnath/o
#20 hepat/o
hepat/o is the combining form that refers to "liver".
Located in the right upper abdomen below the rib cage, the liver is the largest internal organ in the body. As well as removing toxins from the body's blood supply, it regulates normal blood sugar levels, controls blood clotting, among other functions.
Examples of Medical Terms Containing hepat/o
Hepatitis: hepat ( "liver") + -itis ( "inflammation")
Definition: Inflammation of the liver, which can be caused by viral infections, alcohol consumption, or other factors. It can cause symptoms such as fatigue, jaundice, and abdominal pain.
Hepatocellular: hepat/o ( "liver") + -cellular ( "related to cells")
Definition: Pertaining to liver cells. A type of liver cancer that begins in liver cells is hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
Hepatomegaly: hepat/o ( "liver") + -megaly ( "enlargement")
Definition: Enlargement of the liver, usually caused by liver disease, cancer, or metabolic disorders.
Hepatorenal: hepat/o ( "liver") + ren ( "kidney") + -al ("pertaining to" or "related to")
Definition: Pertaining to liver and kidney, it is a term used to describe the functional impairment of the kidney that occurs in patients with liver cirrhosis.
Hepatotoxicity: hepat/o ( "liver") + toxic ( "poisonous") + -ity ( "state or condition of")
Definition: Toxicity to the liver, which can be caused by medications, chemicals, or other toxins and can lead to liver damage or failure.
Hepatocyte: hepat/o ( "liver") + -cyte ( "cell")
Definition: A liver cell, the primary functional unit of the liver, responsible for the synthesis, metabolism and storage of various substances.
Hepatic: hepat/o ( "related to the liver") + -ic ("pertaining to")
Definition: Pertaining to the liver, as in the hepatic artery or hepatic vein.
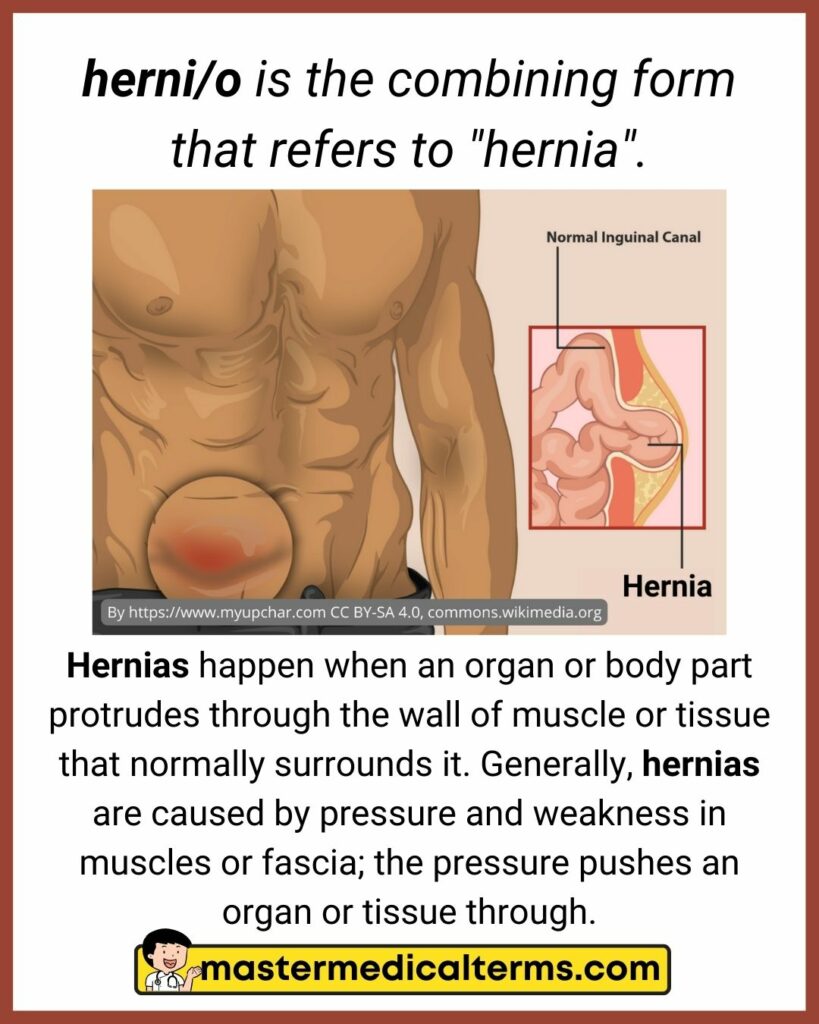
#21 herni/o
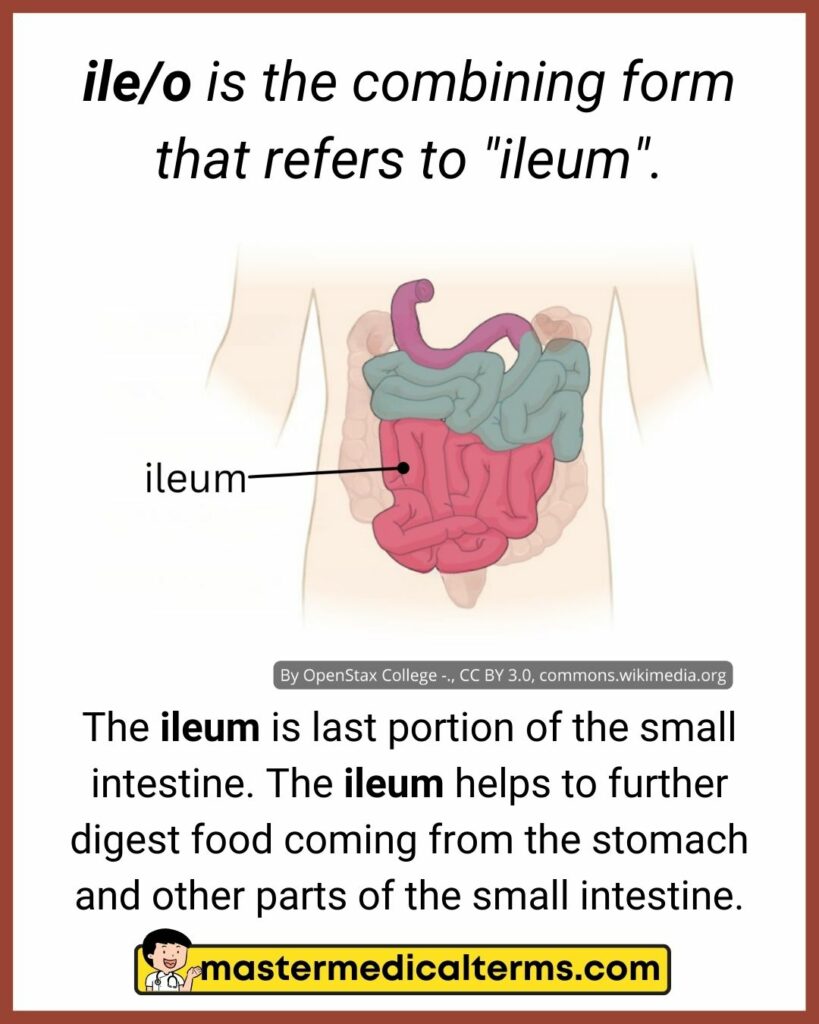
#22 ile/o
#23 jejun/o
#24 labi/o, cheil/o
#25 lingu/o, gloss/o
#26 or/o, stoma, stomat/o
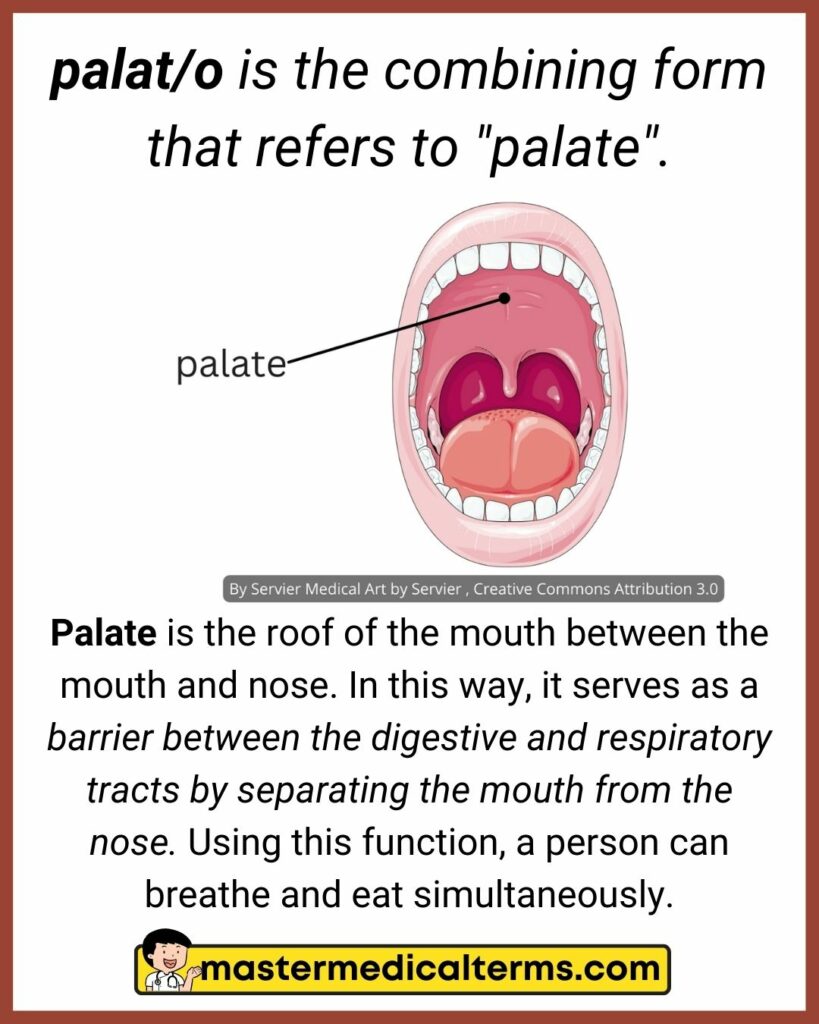
#27 palat/o
palat/o is the combining form that refers to "palate".
Palate is the roof of the mouth between the mouth and nose. In this way, it serves as a barrier between the digestive and respiratory tracts by separating the mouth from the nose. Using this function, a person can breathe and eat simultaneously.
#28 pancreat/o
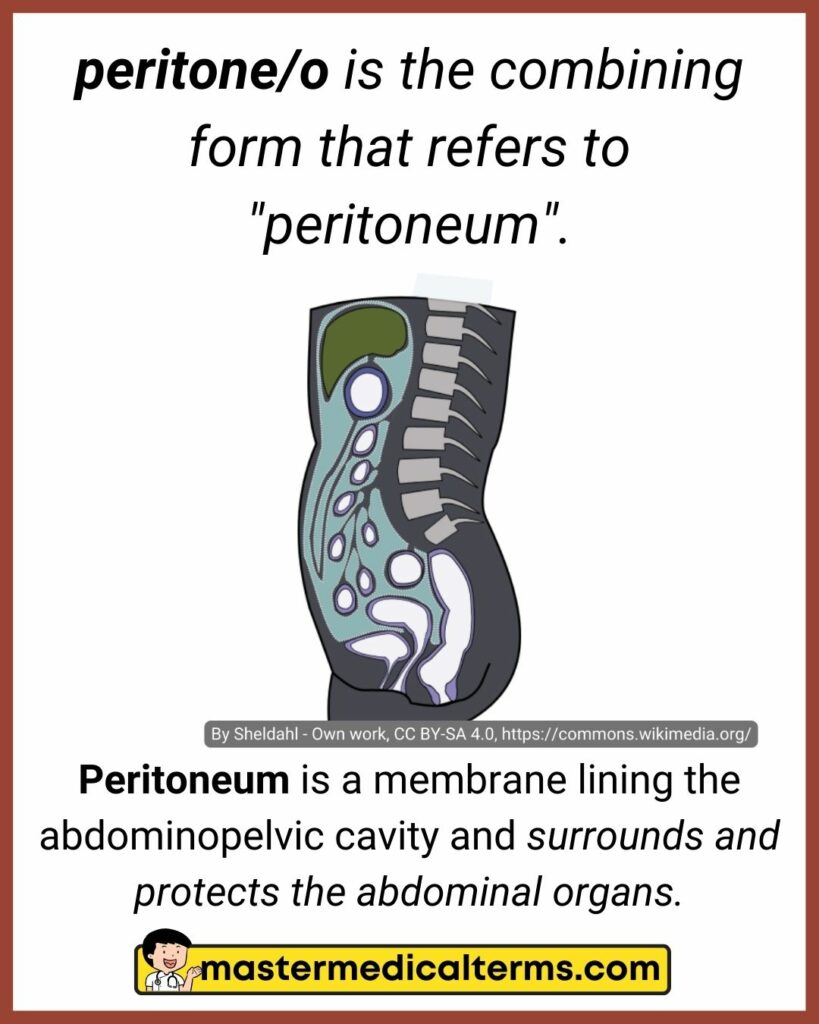
#29 peritone/o
#30 pylor/o
pylor/o is the combining form that refers to "pylorus" or "pyloric sphincter".
Pylorus or pyloric part, connects stomach to duodenum (first part of small intestine). During digestion, the pylorus opens and closes, thus enabling partially digested food to pass from the stomach to the small intestine.
#31 rect/o, proct/o
#32 sial/o
sial/o is the combining form that refers to "saliva", "salivary gland" or "salivary duct".
Each salivary gland is located on one side of the face. They produce saliva (also called spit), which serves as the lubricating substance for the mouth and throat. Saliva contains enzymes that initiate digestion of foods as soon as they enter the mouth. Furthermore, it contains antibodies that protect against infections of the mouth and throat.
#33 sigmoid/o
#34 steat/o
steat/o is the combining form that refers to "fat".
Fats belong to a group of compounds known as lipids that are found in the body and are hydrophobic (insoluble in water). The fat in the body gives the body energy, protects the organs, supports cell growth, maintains cholesterol levels, and helps the body absorb nutrients.