This set of flashcards contains medical prefixes used to describe the degree of a medical term. Each prefix is explained with a word example and a breakdown.
Check out the quiz version of this flashcard if you want to see how much you remembered.
#1 hypo-, hyp-
The medical prefix term hyp(o)- means "low, below normal".
Example Word: hyp(o)/therm/ia
Word Breakdown: Hyp(o)- means "low, below normal", therm is a word root that refers to "heat", and -ia is a suffix term that signifies "condition".
Definition: Hypothermia is characterized by abnormally low body temperatures, particularly below 35 degrees Celsius.
More Examples of Medical Terms Starting with Hypo-
Hypoglycemia: hypo- ( "low or below normal") + ( "sugar" or "related to glucose") + -emia ( "related to blood")
Definition: A condition characterized by low levels of glucose (sugar) in the blood, which can cause symptoms such as fatigue, weakness, and confusion.
Hypotension: hypo- ( "low or below normal") + -tension ( "pressure")
Definition: A condition characterized by low blood pressure, which can cause symptoms such as dizziness, fainting, and fatigue.
Hypothyroidism: hypo- ( "low or below normal") + thyroid ( "related to the thyroid gland") + -ism ( "condition")
Definition: A condition that is characterized by underactivity of the thyroid gland, which can result in symptoms such as weakness, weight gain, and sensitivity to cold weather.
Hypoxemia: hypo- ( "low or below normal") + ox/i ( "oxygen") + -emia ( "related to blood")
Definition: A condition characterized by low levels of oxygen in the blood, which can cause symptoms such as shortness of breath and fatigue.
Hypovolemia: hypo- ( "low or below normal") + vol ( "volume") + -emia ( "related to blood")
Definition: A condition characterized by low blood volume, which can cause symptoms such as lightheadedness, dizziness, and fainting.
Hypocholesterolemia: hypo- ( "low or below normal") + cholesterol ( "related to cholesterol levels in the blood") + -emia ( "related to blood")
Definition: A condition characterized by low levels of cholesterol in the blood, which is generally considered a healthy condition.
Hyponatremia: hypo-( "low or below normal") + natr ( "sodium") + -emia ( "related to blood")
Definition: A condition characterized by low levels of sodium in the blood, which can cause symptoms such as confusion, muscle weakness, and seizures.
Hypokalemia: hypo- ( "low or below normal") + kal ("potassium") + -emia ( "related to blood")
Definition: A condition characterized by low levels of potassium in the blood, which can cause symptoms such as muscle weakness, cramping, and irregular heartbeats.
Hypocalcemia: hypo- ( "low or below normal") + calc ("calcium") + -emia ( "related to blood")
Definition: A condition characterized by low levels of calcium in the blood, which can cause symptoms such as muscle cramps, spasms, and numbness and tingling in the fingers and toes.
Hypomagnesemia: hypo- ( "low or below normal") + magnes ( "magnesium") + -emia ( "related to blood")
Definition: A condition characterized by low levels of magnesium in the blood, which can cause symptoms such as muscle weakness, cramps, and irregular heartbeats.
Hypophosphatemia: hypo- ( "low or below normal") + phosphat ("phosphorus") + -emia ( "related to blood")
Definition: A condition characterized by low levels of phosphorus in the blood, which can cause symptoms such as muscle weakness, fatigue, and bone pain.
#2 hyper-
The medical prefix term hyper- means "high, above normal".
Example Word: hyper/therm/ia
Word Breakdown: Hyper- means "high, above normal", therm is a word root that refers to "heat", and -ia is a suffix term that signifies "condition".
Definition: Hyperthermia is an abnormally elevated body temperature due to a failure of the body's heat-regulating mechanisms.
More Examples of Medical Terms Starting with Hyper-
Hyperglycemia: hyper- ( "high or above normal") + glyc ( "sugar" or "related to glucose") + -emia ( "related to blood")
Definition: A disorder characterized by high levels of glucose (sugar) in the blood, resulting in symptoms such as excessive thirst, frequent urination, and blurry vision.
Hypertension: hyper- ( "high or above normal") + -tension ( "pressure")
Definition: A condition characterized by high blood pressure, which can cause symptoms such as headaches, shortness of breath, and increased risk of heart attack or stroke.
Hyperthyroidism: hyper- ( "high or above normal") + thyroid ( "related to the thyroid gland") + -ism ( "condition")
Definition: A disorder in which the thyroid gland is excessively active, resulting in loss of weight, rapid heartbeats, and shaking.
Hyperoxemia: hyper- ( "high or above normal") + ox/i ( "oxygen") + -emia ( "related to blood")
Definition: A condition characterized by high levels of oxygen in the blood, which can cause symptoms such as increased breathing rate, decreased blood pressure, and headaches.
Hypervolemia: hyper- ( "high or above normal") + vol ( "volume") + -emia ( "related to blood")
Definition: A condition characterized by high blood volume, which can cause symptoms such as swelling and an increased risk of heart failure.
Hypercholesterolemia: hyper- ( "high or above normal") + cholesterol ( "related to cholesterol levels in the blood") + -emia ( "related to blood")
Definition: A condition characterized by high levels of cholesterol in the blood, which can increase the risk of heart disease and stroke.
Hypernatremia: hyper- ( "high or above normal") + natr ( "sodium") + -emia ( "related to blood")
Definition: A condition characterized by high levels of sodium in the blood, which can cause symptoms such as confusion, muscle weakness, and seizures.
Hyperkalemia: hyper- ( "high or above normal") + kal ("potassium") + -emia ( "related to blood")
Definition: A condition characterized by high levels of potassium in the blood, which can cause symptoms such as muscle weakness, cramping, and irregular heartbeats.
Hypercalcemia: hyper- ( "high or above normal") + calc ("calcium") + -emia ( "related to blood")
Definition: A condition characterized by high levels of calcium in the blood, which can cause symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, and kidney damage.
Hypermagnesemia: hyper- ( "high or above normal") + magnes ( "magnesium") + -emia ( "related to blood")
Definition: A condition characterized by high levels of magnesium in the blood, which can cause symptoms such as muscle weakness, confusion, and irregular heartbeats.
Hyperphosphatemia: hyper- ( "high or above normal") + phosphat ("phosphorus") + -emia ( "related to blood")
Definition: A condition characterized by high levels of phosphorus in the blood, which can cause symptoms such as itchy skin, bone pain, and an increased risk of kidney damage.
#3 norm(o)-
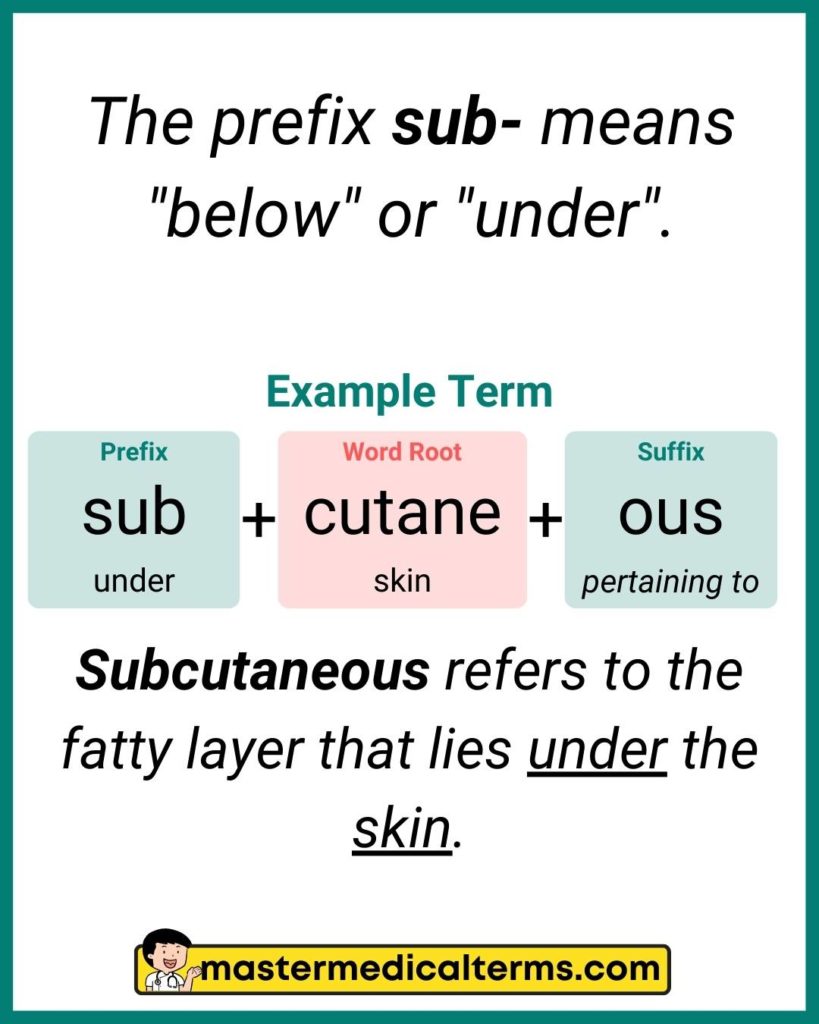
#4 sub-
Sub- is a medical prefix term that means "low, below normal".
Example Word: sub/cutane/ous
Word Breakdown: In this case, sub- means "low, below normal", cutane is a word root that means "skin," and -ous is a suffix that means "pertaining to".
Definition: The subcutaneous layer refers to the fatty layer under the skin.
#5 super-
The medical prefix term super- means "high, above normal".
Example Word: super/ego
Word Breakdown: Super- means "high, above normal", eg/o is a combining form that refers to "self".
Definition: The superego is the part of the mind that works as a self-reflective conscience, evaluating social standards.
#6 ultra-
The medical prefix term ultra- means "high, above normal".
Example Word: ultra/sono/graphy
Word Breakdown: Ultra- means "high, above normal", son/o is a combining form that refers to "sound", -graphy is a suffix term that indicates "process of recording".
Definition: Ultrasonography is a form of imaging that utilizes high-frequency sound (ultrasound waves) to obtain images of internal organs or fetus.